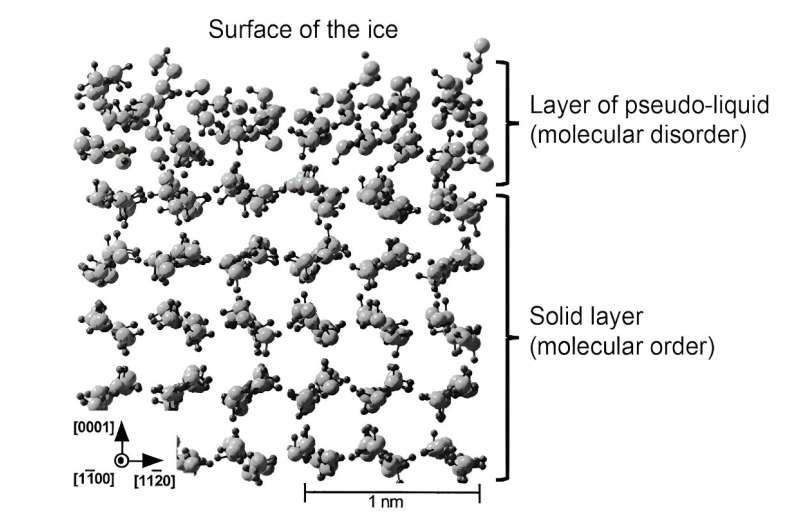
Modelling of the structure of ice where we can see the structural disorder specific to liquids over a thickness of one to two molecules. Deeper into the ice, we find the ordered (crystalline) structure of ice. Credit: Philippe Brunet, adapted from T. Ikeda-Fukazawa and K. Kawamura, Fourni par l’auteur
Whether in the form of frost or a smooth, transparent ice cube, ice adheres spontaneously and even quite strongly to many solid surfaces. However, as any careless person who has skidded on a winter sidewalk can testify, ice can also be very slippery. In fact, ice can be both sticky and slippery.
This versatility has long puzzled scientists. To begin with, they have been attempting to crack the secret behind ice’s slipperiness for more than 150 years. Among them have been famous physicists such as Lord Kelvin and Michael Faraday. The latter, better known for his work in electromagnetism, was the first to envisage the presence of a thin layer of liquid water covering ice, even well below 0°C. At the time, he reasoned that the contact of a solid object against the surface layer prompted it to act as a lubricant, greatly reducing friction on the ice. The existence of this liquid layer was confirmed by experiments more than a century later.
A slippery matter
To answer the question “Why is ice slippery?” we first need to understand how this thin layer of liquid water onto the frozen surface has come into being.
As water is denser in its liquid phase than in its icy state, it was long thought that the melting of the ice surface was linked to excess pressure—for example, due to the weight of the skater on the small surface area lying beneath her or his skates. By compressing the ice further, the skater would cause it to melt, rendering it liquid and slippery.
Others believe heat is released by friction as the object moves over the ice, causing the surface to melt. Much as when you rub your hands together to warm them, when you rub one solid against another, they heat up.
However, these two mechanisms do not explain why ice remains slippery below -20°C. At such temperatures, it would take considerable pressure—around 500 times that exerted by an ice skate—to cause it to melt.
In the 1960s, more than a century after Faraday, J.W. Telford and J.S. Turner slowly pulled a wire through “cold” ice (below -20°C) to reveal that it remained slippery down to -35°C, at which point the heat released by friction no longer sufficed to melt the ice.
It was only about a century after Faraday’s intuition that we were able to demonstrate this liquid layer indirectly, by measuring properties of the ice’s surface and not the volume—in this case its properties of absorption of hydrocarbon vapors, which are quite comparable to those of liquid water!
Techniques involving proton or X-ray scattering, usually used to study the structure of crystals, have made it possible to estimate the thickness at between one and several hundred nanometers. Some studies have even suggested that this thickness diverges as the temperature approaches 0°C.
More recently, simulations have made it possible to better represent the structure of this liquid layer. Subsequently, this layer was referred to as “pseudo-liquid” or “quasi-liquid” to differentiate it from the true liquid phase. Such theoretical work has shown that in this surface layer, the molecules are able to move more freely, confirming its role as a lubricant. Nevertheless, the molecular structure is not exactly the same as that of liquid water, which has consequences for the mechanical properties of this pseudo-liquid layer.
A recent study showed a strong correlation between the individual mobility of the molecules and the macroscopic coefficient of friction (the lower the coefficient, the easier it is to glide), suggesting that it is not so much the thickness of the layer that matters for gliding but rather the individual movement of the molecules. The minimum value of the coefficient of friction is measured at -7°C, known as the optimal temperature for skiers and skaters.
Other research went to the heart of the pseudo-liquid layer using a nano-probe, the tip of an atomic force microscope. By vibrating this tip connected to an extremely precise force sensor, measuring the friction between the tip and the liquid in the layer, the authors measured that this liquid can be 50 times more viscous than liquid water, and that it also possesses elasticity (a property more associated with the solid state). This viscosity is similar to that of your edible oils, making the pseudo-liquid layer an excellent lubricant.
To sum up: ice slips because a liquid layer of about 1 to 100 nanometers thick forms on its surface. Its mechanical properties (viscosity, elasticity), which are different from those of liquid water, and the mobility of the molecules that make it up, which is much greater than that of solid ice, give it its exceptional lubricating properties.
Why does ice stick?
Ice’s stickiness, however, continues to confound scientists, notwithstanding 70 years of experiments. During the latter, scientists have tended to make use of a rather simple kit: a piston connected to force sensor pushes a block of ice, itself stuck to a solid object. When the ice cube breaks away, the force recorded by the sensor suddenly becomes zero, and the maximum value before this breakaway is measured. But these results have shown sometimes contradictory trends, and a fairly wide dispersion.
A recent review on the subject concluded that the adhesion force of ice “depends not only on the chemical composition, surface roughness, mechanical and thermal properties of the substrate [but] also depends critically on the temperature and even on the experimental device for measuring adhesion.”
To be a little more precise, when we explore the literature on the subject over the last 60 years, we note that the strength with which ice sticks to a solid depends strongly on temperature in a range between -20°C and 0°C (ice sticks harder to a colder solid). As for the role of surface roughness, it is ambivalent: for some solids (particularly metals), ice sticks more strongly to a rougher substrate, whereas on some plastics it’s the other way round…
Finally, at a chemical level, liquid water may be able spread out better on some surfaces than others. For example, water spreads very well on clean glass, while some surfaces are hydrophobic, such as Teflon.
A recent study has shown that the more water in its liquid state spreads over the surface of a solid, the more ice will adhere to this solid. Conversely, a surface with little affinity for liquid water will also have little adhesion for ice.
Why this relationship between the spread of water and the adhesion of ice? First, for ice to adhere to a cold solid, water in its liquid state must have been able to freeze on contact with the solid. Here’s a simple experiment that anyone can do:
Place a metal plate in the freezer or in your ice cube tray.
Take an ice cube and place it on the plate without taking the whole thing out of the freezer: it won’t stick.
Take another ice cube and let it melt slightly at room temperature (by taking it out of the freezer for a few seconds, for example), then place it on the cold plate. This time it sticks!
What can we conclude? Intuitively, the greater the affinity of the water for the surface, the more easily the liquid water seeps into the roughness and gaps on the surface of the solid, increasing the contact surface between it and the ice after solidification, thus consolidating the adhesion. This experiment also demonstrates the role of liquid water as an adhesive. When you use a conventional adhesive—say, liquid glue—to join two parts together, it is when the parts solidify (by the evaporation of a solvent in the glue) that the strong, definitive adhesion takes place. The same thing happens when liquid water cools on contact with a cold solid and solidifies. The layer of frozen water then plays the role of one of the solids.
How can the ice be made less adhesive?
We can’t explain ice adhesion in detail, but we can try to reduce its strength. The idea of using water-repellent treatments has naturally emerged, but these treatments are not very robust over time and can have the opposite effect of what was intended. More promising solutions involve spreading a thin layer of oil or a hydrogel over the surface, but there are still problems with the stability of these layers over large areas.
Another approach is to use active de-icing methods. One such technique is surface ultrasound, which generates “micro-earthquakes” on the solid surface and can cause the ice to break away. We are currently studying this method in the MSC laboratory.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()
Citation:
The sticking point: Why physicists are still struggling to understand ice’s capacity to adhere and become slippery (2024, March 21)
retrieved 21 March 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-03-physicists-struggling-ice-capacity-adhere.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
>>> Read full article>>>
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source : Phys.org – https://phys.org/news/2024-03-physicists-struggling-ice-capacity-adhere.html










