Research shows interstitial macrophages are unexpectedly the primary target for SARS-CoV-2 in the lungs, leading to severe COVID-19, suggesting new therapeutic targets. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
A previously overlooked type of immune cell allows SARS-CoV-2 to proliferate, Stanford Medicine scientists have found. The discovery has important implications for preventing severe COVID-19.
The lung cell type that’s most susceptible to infection by SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is not the one previously assumed to be most vulnerable. What’s more, the virus enters this susceptible cell via an unexpected route. The medical consequences may be significant.
Stanford Medicine investigators have implicated a type of immune cell known as an interstitial macrophage in the critical transition from a merely bothersome COVID-19 case to a potentially deadly one. Interstitial macrophages are situated deep in the lungs, ordinarily protecting that precious organ by, among other things, engorging viruses, bacteria, fungi and dust particles that make their way down our airways. But it’s these very cells, the researchers have shown in a study that was published on April 10 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, that of all known types of cells composing lung tissue are most susceptible to infection by SARS-CoV-2.
SARS-CoV-2-infected interstitial macrophages, the scientists have learned, morph into virus producers and squirt out inflammatory and scar-tissue-inducing chemical signals, potentially paving the road to pneumonia and damaging the lungs to the point where the virus, along with those potent secreted substances, can break out of the lungs and wreak havoc throughout the body.
The surprising findings point to new approaches in preventing a SARS-CoV-2 infection from becoming a life-threatening disease. Indeed, they may explain why monoclonal antibodies meant to combat severe COVID didn’t work well, if at all — and when they did work, it was only when they were administered early in the course of infection, when the virus was infecting cells in the upper airways leading to the lungs but hadn’t yet ensconced itself in lung tissue.
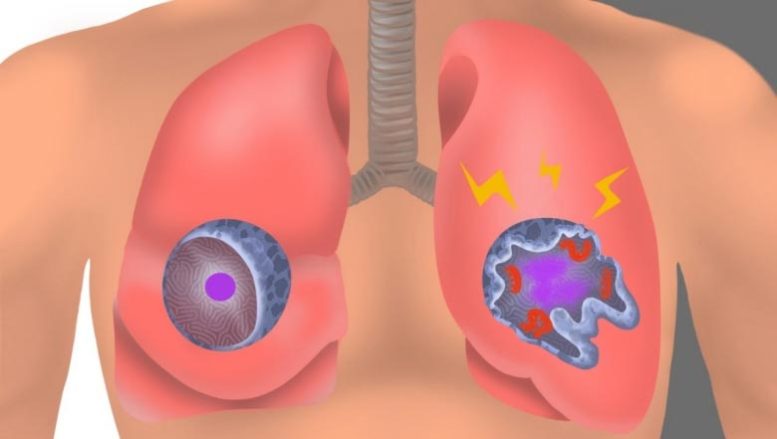
In an uninfected interstitial macrophage, the nucleus (purple) and outer cell membrane (blue) are intact. In an infected interstitial macrophage, the nucleus is shattered, copious newly made viral components (red) clump together, and the cell broadcasts inflammatory and scar-tissue-inducing chemical signals (yellow). Credit: Emily Moskal
The Virus Surprises
“We’ve overturned a number of false assumptions about how the virus actually replicates in the human lung,” said Catherine Blish, MD, PhD, a professor of infectious diseases and of microbiology and immunology and the George E. and Lucy Becker Professor in Medicine and associate dean for basic and translational research.
Blish is the co-senior author of the study, along with Mark Krasnow, MD, PhD, the Paul and Mildred Berg Professor of biochemistry and the Executive Director of the Vera Moulton Wall Center for Pulmonary Vascular Disease.
“The critical step, we think, is when the virus infects interstitial macrophages, triggering a massive inflammatory reaction that can flood the lungs and spread infection and inflammation to other organs,” Krasnow said. Blocking that step, he said, could prove to be a major therapeutic advance. But there’s a plot twist: The virus has an unusual way of getting inside these cells — a route drug developers have not yet learned how to block effectively — necessitating a new focus on that alternative mechanism, he added.
In a paper published in Nature in early 2020, Krasnow and his colleagues including then-graduate student Kyle Travaglini, PhD — who is also one of the new study’s co-lead authors along with MD-PhD student Timothy Wu — described a technique they’d worked out for isolating fresh human lungs; dissociating the cells from one another; and characterizing them, one by one, on the basis of which genes within each cell were active and how much so. Using that technique, the Krasnow lab and collaborators were able to discern more than 50 distinct cell types, assembling an atlas of healthy lung cells.
“We’d just compiled this atlas when the COVID-19 pandemic hit,” Krasnow said. Soon afterward, he learned that Blish and Arjun Rustagi, MD, PhD, instructor of infectious diseases and another lead co-author of the study, were building an ultra-safe facility where they could safely grow SARS-CoV-2 and infect cells with it.
A collaboration ensued. Krasnow and Blish and their associates obtained fresh healthy lung tissue excised from seven surgical patients and five deceased lung donors whose lungs were virus-free but for one reason or another not used in transplants. After infecting the lung tissue with SARS-CoV-2 and waiting one to three days for the infection to spread, they separated and typed the cells to generate an infected-lung-cell atlas, analogous to the one Krasnow’s team had created with healthy lung cells. They saw most of the cell types that Krasnow’s team had identified in healthy lung tissue.
Now the scientists could compare pristine versus SARS-CoV-2-infected lungs cells of the same cell type and see how they differed: They wanted to know which cells the virus infected, how easily SARS-CoV-2 replicated in infected cells, and which genes the infected cells cranked up or dialed down compared with their healthy counterparts’ activity levels. They were able to do this for each of the dozens of different cell types they’d identified in both healthy and infected lungs.
“It was a straightforward experiment, and the questions we were asking were obvious,” Krasnow said. “It was the answers we weren’t prepared for.”
It’s been assumed that the cells in the lungs that are most vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2 infection are those known as alveolar type 2 cells. That’s because the surfaces of these cells, along with those of numerous other cell types in the heart, gut and other organs, sport many copies of a molecule known as ACE2. SARS-CoV-2 has been shown to be able to grab onto ACE2 and manipulate it in a way that allows the virus to maneuver its way into cells.
Alveolar type 2 cells are somewhat vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2, the scientists found. But the cell types that were by far the most frequently infected turned out to be two varieties of a cell type called a macrophage.
Virus Factories
The word “macrophage” comes from two Greek terms meaning, roughly, “big eater.” This name is not unearned. The air we inhale carries not only oxygen but, unfortunately, tiny airborne dirt particles, fungal spores, bacteria and viruses. A macrophage earns its keep by, among other things, gobbling up these foreign bodies.
The airways leading to our lungs culminate in myriad alveoli, minuscule one-cell-thick air sacs, which are abutted by abundant capillaries. This interface, called the interstitium, is where oxygen in the air we breathe enters the bloodstream and is then distributed to the rest of the body by the circulatory system.
The two kinds of SARS-CoV-2-susceptible lung-associated macrophages are positioned in two different places. So-called alveolar macrophages hang out in the air spaces within the alveoli. Once infected, these cells smolder, producing and dribbling out some viral progeny at a casual pace but more or less keeping a stiff upper lip and maintaining their normal function. This behavior may allow them to feed SARS-CoV-2’s progression by incubating and generating a steady supply of new viral particles that escape by stealth and penetrate the layer of cells enclosing the alveoli.
Interstitial macrophages, the other cell type revealed to be easily and profoundly infected by SARS-CoV-2, patrol the far side of the alveoli, where the rubber of oxygen meets the road of red blood cells. If an invading viral particle or other microbe manages to evade alveolar macrophages’ vigilance, infect and punch through the layer of cells enclosing the alveoli, jeopardizing not only the lungs but the rest of the body, interstitial macrophages are ready to jump in and protect the neighborhood.
At least, usually. But when an interstitial macrophage meets SARS-CoV-2, it’s a different story. Rather than get eaten by the omnivorous immune cell, the virus infects it.
And an infected interstitial macrophage doesn’t just smolder; it catches on fire. All hell breaks loose as the virus literally seizes the controls and takes over, hijacking a cell’s protein- and nucleic-acid-making machinery. In the course of producing massive numbers of copies of itself, SARS-CoV-2 destroys the boundaries separating the cell nucleus from the rest of the cell like a spatula shattering and scattering the yolk of a raw egg. The viral progeny exit the spent macrophage and move on to infect other cells.
But that’s not all. In contrast to alveolar macrophages, infected interstitial macrophages pump out substances that signal other immune cells elsewhere in the body to head for the lungs. In a patient, Krasnow suggested, this would trigger an inflammatory influx of such cells. As the lungs fill with cells and fluid that comes with them, oxygen exchange becomes impossible. The barrier maintaining alveolar integrity grows progressively damaged. Leakage of infected fluids from damaged alveoli propels viral progeny into the bloodstream, blasting the infection and inflammation to distant organs.
Yet other substances released by SARS-CoV-2-infected interstitial macrophages stimulate the production of fibrous material in connective tissue, resulting in scarring of the lungs. In a living patient, the replacement of oxygen-permeable cells with scar tissue would further render the lungs incapable of executing oxygen exchange.
“We can’t say that a lung cell sitting in a dish is going to get COVID,” Blish said. “But we suspect this may be the point where, in an actual patient, the infection transitions from manageable to severe.”
Another Point of Entry
Compounding this unexpected finding is the discovery that SARS-CoV-2 uses a different route to infect interstitial macrophages than the one it uses to infect the other types.
Unlike alveolar type 2 cells and alveolar macrophages, to which the virus gains access by clinging to ACE2 on their surfaces, SARS-CoV-2 breaks into interstitial macrophages using a different receptor these cells display. In the study, blocking SARS-CoV-2’s binding to ACE2 protected the former cells but failed to dent the latter cells’ susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
“SARS-CoV2 was not using ACE2 to get into interstitial macrophages,” Krasnow said. “It enters via another receptor called CD209.”
That would seem to explain why monoclonal antibodies developed specifically to block SARS-CoV-2/ACE2 interaction failed to mitigate or prevent severe COVID-19 cases.
It’s time to find a whole new set of drugs that can impede SARS-CoV-2/CD209 binding. Now, Krasnow said.
Reference: “Interstitial macrophages are a focus of viral takeover and inflammation in COVID-19 initiation in human lung ” by Timothy Ting-Hsuan Wu, Kyle J. Travaglini, Arjun Rustagi, Duo Xu, Yue Zhang, Leonid Andronov, SoRi Jang, Astrid Gillich, Roozbeh Dehghannasiri, Giovanny J. Martínez-Colón, Aimee Beck, Daniel Dan Liu, Aaron J. Wilk, Maurizio Morri, Winston L. Trope, Rob Bierman, Irving L. Weissman, Joseph B. Shrager, Stephen R. Quake, Christin S. Kuo, Julia Salzman, W.E. Moerner, Peter S. Kim, Catherine A. Blish and Mark A. Krasnow, 10 April 2024, Journal of Experimental Medicine.
DOI: 10.1084/jem.20232192
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health (grants K08AI163369, T32AI007502, and T32DK007217), the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Chan Zuckerberg Biohub, the Burroughs Wellcome Fund, Stanford Chem-H, the Stanford Innovative Medicine Accelerator, and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
>>> Read full article>>>
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source : SciTechDaily – https://scitechdaily.com/stanford-medicine-unmasks-the-surprising-instigators-of-severe-covid-in-the-lungs/










