
Researchers at Princeton University have made a breakthrough in understanding kinetic magnetism by using ultracold atoms in a laser-built lattice to image a new type of polaron, revealing how impurity motion in an atomic array causes robust magnetism at high temperatures. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
Physicists from Princeton University directly imaged the microscopic object responsible for this magnetism, an unusual type of polaron.
Not all magnets are the same. When we think of magnetism, we usually think of magnets that stick to a refrigerator’s door. For these types of magnets, the electronic interactions that give rise to magnetism have been understood for around a century, since the early days of quantum mechanics. But there are many different forms of magnetism in nature, and scientists are still discovering the mechanisms that drive them.
Now, physicists from Princeton University have made a major advance in understanding a form of magnetism known as kinetic magnetism, using ultracold atoms bound in an artificial laser-built lattice. Their experiments, chronicled in a paper published this week in the journal Nature, allowed the researchers to directly image the microscopic object responsible for this magnetism, an unusual type of polaron, or quasiparticle that emerges in an interacting quantum system.
Understanding Kinetic Magnetism
“This is very exciting,” said Waseem Bakr, professor of physics at Princeton and the senior author of the paper. “The origins of the magnetism have to do with the motion of impurities in the atomic array, hence the name kinetic magnetism. This motion is highly unusual and leads to magnetism that is robust even at very high temperatures. Combined with the tunability of the magnetism with doping—the addition or removal of particles—kinetic magnetism is very promising for device applications in real materials.”
Bakr and his team studied this novel form of magnetism on a level of detail unrealized in previous research. With the control afforded by ultracold atomic systems, the researchers have been able to visualize, for the first time, the finely-grained physics that gives rise to kinetic magnetism.
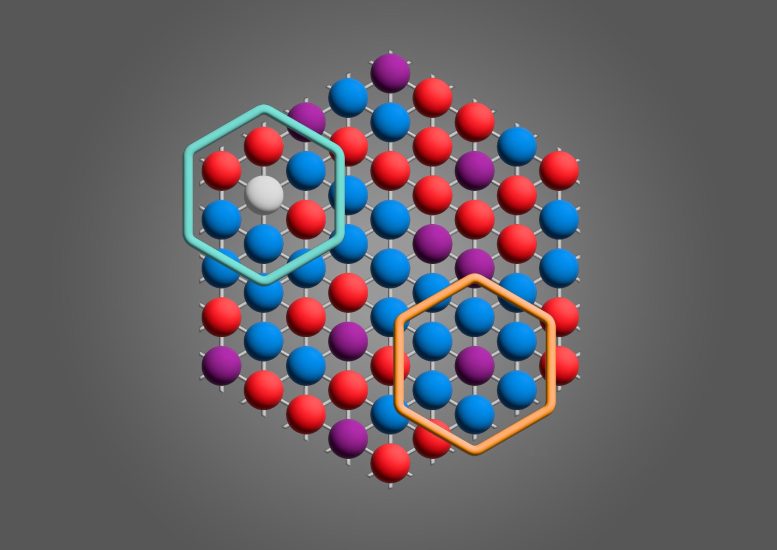
Researchers at Princeton have directly imaged the microscopic origins of a novel type of magnetism. Credit: Max Prichard, Waseem Bakr group at Princeton University
Advanced Tools for Quantum Discoveries
“We have the capability in our lab to look at this system at the single atom and single site level in the lattice and take ‘snapshots’ of the subtle quantum correlations between the particles in the system,” Bakr said.
For several years, Bakr and his research team have studied quantum states by experimenting with ultracold subatomic particles known as fermions in a vacuum chamber. They have devised a sophisticated apparatus that cools atoms to ultracold temperatures and loads them into artificial crystals known as optical lattices created using laser beams. This system has allowed the researchers to explore many interesting aspects of the quantum world involving the emergent behavior of ensembles of interacting particles.
Theoretical Foundations and Experimental Insights
One early theoretically proposed mechanism for magnetism that laid the groundwork for the team’s current experiments is known as Nagaoka ferromagnetism, named for its discoverer Yosuke Nagaoka. Ferromagnets are ones in which the electrons’ spin states all point in the same direction.
While a ferromagnet with aligned spins is the most familiar type of magnet, in the simplest theoretical setting, strongly interacting electrons on a lattice actually tend towards antiferromagnetism, in which the spins align in alternating directions. This preference for anti-alignment of neighboring spins occurs as the result of an indirect coupling of neighboring electron spins known as superexchange.
However, Nagaoka theorized that ferromagnetism may also result from a totally different mechanism, one determined by the motion of intentionally added impurities, or dopants. This can best be understood by imagining a two-dimensional square lattice in which each lattice site, with one exception, is occupied by an electron. The unoccupied site (or hole dopant) wanders around in the lattice.
Nagaoka found that if the hole moves in an environment of aligned spins or a ferromagnet, the different trajectories for the motion of the hole quantum mechanically interfere with each other. This enhances the spreading out of the hole’s quantum position and reduces the kinetic energy, a favorable outcome.
Nagaoka’s Legacy and Modern Quantum Mechanics
Nagaoka’s theorem quickly gained recognition because there are few rigorous proofs purporting to explain ground states of systems of strongly interacting electrons. But observing the consequences through experiments posed a difficult challenge owing to the strict requirements of the model. In the theorem, the interactions needed to be infinitely strong and only a single dopant was allowed. Over five decades after Nagaoka proposed his theory, other researchers realized that these unrealistic conditions could be relaxed significantly in lattices with a triangular geometry.
The Quantum Experiment and Its Implications
To conduct the experiment, the researchers used vapors of lithium-6 atoms. This isotope of lithium contains three electrons, three protons, and three neutrons. “The odd total number makes this a fermionic isotope, which means that the atoms behave similarly to electrons in a solid-state system,” said Benjamin Spar, a graduate student in physics at Princeton University and a co-lead author of the paper.
When these gases are cooled down using laser beams to extreme temperatures only a few billionths of a degree above absolute zero, their behavior begins to be governed by the principles of quantum mechanics rather than the more familiar classical mechanics.
Exploring Quantum States Through Cold Atom Setups
“Once we’ve achieved this quantum system, the next thing we do is load the atoms into the triangular optical lattice. In the cold atom setup, we can control how fast atoms move around or how strongly they interact with each other,” said Spar.
In many strongly interacting systems, the particles in a lattice are organized into a “Mott insulator,” which is a state of matter in which a single particle occupies each site of the lattice. In this state, there are weak antiferromagnetic interactions due to superexchange between the spin of electrons on neighboring sites. But instead of using a Mott insulator, the researchers used a technique called “doping,” which either removes some particles, thereby leaving “holes” in the lattice, or adds extra particles.
Unveiling New Forms of Quantum Magnetism
“We don’t start with one atom per site in our experiment,” said Bakr. “Instead, we dope the lattice with holes or particles. And when you do this, you find that there is a much more robust form of magnetism that is observed in these systems with higher energy scale than the usual superexchange magnetism. This energy scale has to do with hopping of the atoms in the lattice.”
Leveraging the much larger lattice site spacings in optical lattices compared to real materials, the researchers were able to see what was occurring on the single-site level with an optical microscope. They found that the objects responsible for this new form of magnetism are a new type of magnetic polaron.
The Role of Polarons in Quantum Systems
“A polaron is a quasiparticle that emerges in a quantum system with many interacting constituents,” said Bakr. “It acts very much like a regular particle, in the sense it has properties like a charge, a spin, and effective mass, but it is not an actual particle like an atom. In this case, it is a dopant that moves around with a disturbance to its magnetic environment, or how the spins around it are aligned relative to each other.”
In real materials, this new form of magnetism has previously been observed in so-called moiré materials consisting of stacked two-dimensional crystals, and this has only occurred in the last year.
Probing Deeper into Quantum Magnetism
“The probes of magnetism available for these materials are limited. Experiments with moiré materials have measured macroscopic effects, associated with how a large piece of material responds when a magnetic field is applied,” said Spar. “With the cold atom setup, we can dig deep into the microscopic physics responsible for the magnetism. We have taken detailed images revealing the spin correlations around the mobile dopants. For example, we find that a hole dopant surrounds itself with anti-aligned spins as it moves around, while a particle dopant does the opposite, surrounding itself with aligned spins.”
This research has far-reaching implications in condensed matter physics, even beyond understanding the physics of magnetism. For example, more complex versions of these polarons have been hypothesized to lead to mechanisms for hole dopants to pair up, which may result in superconductivity at high temperatures.
Future Directions in Quantum Magnetism Research
“The most exciting part of this research is that it truly is concurrent with studies in the condensed matter community,” said Max Prichard, a graduate student and co-lead author of the paper. “We are in the unique position to provide insight to a timely problem from a totally different angle, and all parties benefit.”
Looking forward, the researchers are already devising new and innovative ways to further probe this new, exotic form of magnetism—and investigate the spin polaron in greater detail.
Next Steps in Polaron Research
“In this first experiment, we’ve simply taken snapshots of the polaron, which is only the first step,” said Prichard. “But we’re now interested in doing a spectroscopic measurement of the polarons. We want to see how long the polarons live in the interacting system, to measure the energy binding together a polaron’s constituents and its effective mass as it propagates in the lattice. There is a lot more to do.”
Other members of the team are Zoe Yan, now at the University of Chicago, and theorists Ivan Morera, University of Barcelona, Spain, and Eugene Demler, Institute of Theoretical Physics in Zurich, Switzerland. The experimental work was supported by the National Science Foundation, the Army Research Office and the David and Lucile Packard Foundation.
Reference: “Directly imaging spin polarons in a kinetically frustrated Hubbard system” by Max L. Prichard, Benjamin M. Spar, Ivan Morera, Eugene Demler, Zoe Z. Yan and Waseem S. Bakr, 8 May 2024, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07356-6
>>> Read full article>>>
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source : SciTechDaily – https://scitechdaily.com/chilling-discoveries-princeton-physicists-unlock-secrets-of-kinetic-magnetism/










