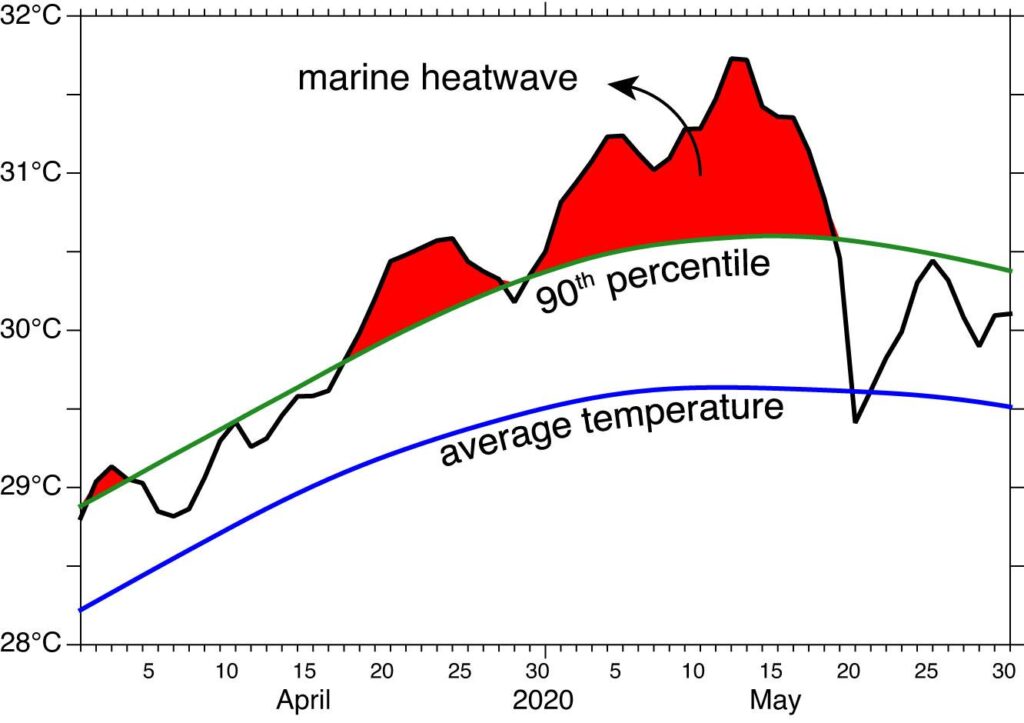
As climate change continues to reshape the Earth’s ecosystems, marine heat waves have emerged as a formidable threat to oceanic life, particularly coastal plankton. The tiny, yet vital organisms serve as the foundational building blocks of marine food webs, supporting everything from small fish to large marine mammals. Recent studies highlighted by Phys.org reveal that these temperature spikes are disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems, leading to unsettling consequences for biodiversity and fisheries. As scientists race to understand the implications of these events, the urgency for actionable solutions becomes increasingly clear. In this article, we delve into the challenges posed by marine heat waves on coastal plankton and explore what this means for the future of our oceans.
Marine Heat Waves Disrupt Coastal Plankton Communities and Ecosystem Health
Recent studies have highlighted the alarming impact of marine heat waves on coastal plankton communities, essential components of marine ecosystems. Elevated water temperatures disrupt the delicate balance of these communities, leading to shifts in species composition and abundance. The repercussions are far-reaching, as plankton serve as the primary food source for a variety of marine life, including fish, mammals, and seabirds. Key findings indicate that during periods of extreme heat, phytoplankton species may thrive at the expense of others, which can destabilize food webs and alter nutrient cycling. This disruption poses significant risks to the health of marine ecosystems, with potential long-term consequences for biodiversity.
In addition to altering community structure, marine heat waves can exacerbate the prevalence of harmful algal blooms (HABs). These blooms can lead to toxic conditions, threatening marine wildlife and human health through contaminated seafood. A recent analysis of data from affected coastal regions reveals the following trends:
| Impact | Effect on Ecosystem |
|---|---|
| Increased Temperature | Shift in plankton species |
| Harmful Algal Blooms | Toxic conditions for marine life |
| Reduced Nutrient Cycling | Impaired food web health |
Coastal ecosystems, often already vulnerable to human impacts, face heightened risks as climate change intensifies the frequency and duration of these heat waves. The integration of effective management strategies aimed at mitigating these effects is crucial to preserving the health of marine environments and the myriad species that depend on them.
Exploring the Consequences of Rising Sea Temperatures on Marine Food Webs
As global temperatures continue to rise, the implications for marine ecosystems are increasingly alarming. Coastal plankton, the foundational elements of marine food webs, are particularly vulnerable to the effects of marine heat waves. These events not only disrupt the typical life cycles of various plankton species but also alter their community structures, leading to cascading effects throughout the food web. Some of the significant consequences include:
- Reduced Biodiversity: Warmer waters can favor certain species of plankton over others, resulting in a decline in biodiversity.
- Altered Nutrient Cycling: Changes in plankton communities can affect nutrient availability, further impacting the overall health of marine ecosystems.
- Impact on Higher Trophic Levels: As primary producers, plankton are critical for sustaining fish populations; their decline can lead to fishing industry challenges.
The relationship between rising sea temperatures and the health of coastal ecosystems is complex and multifaceted. Recent studies have demonstrated the correlation between elevated sea temperatures and diminished rates of phytoplankton productivity, which is critical for sustaining marine life. To better understand this phenomenon, researchers have categorized the impacts as shown in the table below:
| Impact Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Changes | Increased water temperature alters stratification and mixing patterns. |
| Chemical Changes | Higher temperatures may lead to oxygen depletion and altered pH levels. |
| Biological Changes | Species migration and shifts in reproductive cycles rampant due to temperature sensitivity. |
Strategies to Mitigate the Impact of Heat Waves on Plankton Resilience
To effectively address the challenges posed by heat waves on coastal plankton, several strategies ought to be adopted by researchers and policymakers alike. First, monitoring and data collection are critical; establishing comprehensive systems to track temperature fluctuations and plankton health can provide valuable insights into shifts in ecosystems. Additionally, community engagement is essential, fostering collaboration between local fishing communities, scientists, and environmental agencies to raise awareness about the vulnerabilities of plankton to rising temperatures. This grassroots approach can empower community-led initiatives that focus on adaptive management practices aimed at protecting these pivotal marine organisms.
Furthermore, exploring restoration and rehabilitation techniques can play a significant role in bolstering plankton resilience. These may include creating protected marine areas to shield critical breeding grounds from extreme temperature variations, and implementing nutrient management plans to limit the impacts of eutrophication that often accompany heat waves. To visualize the potential benefits of these strategies, the following table outlines various approaches along with their expected outcomes:
| Strategy | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Monitoring Temperature Variations | Improved understanding of plankton responses |
| Community Engagement Programs | Enhanced local stewardship and adaptive practices |
| Protected Marine Areas | Increased biodiversity and plankton survival rates |
| Nutrient Management Plans | Reduced eutrophication and healthier ecosystems |
Insights and Conclusions
As the effects of climate change continue to manifest in our oceans, the implications of marine heat waves stretch far beyond the immediate temperature rise. Coastal plankton, the foundational building blocks of marine ecosystems, are facing unprecedented challenges that threaten their survival and, consequently, the health of marine life and human economies dependent on these vital resources. Scientists urge that understanding and mitigating the consequences of these heat waves is critical to maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance in our oceans. As research advances, it becomes increasingly clear that proactive measures are necessary to combat the profound shifts occurring beneath the surface. The survival of our oceans—and the vital services they provide—rests on our ability to adapt to these changing conditions. Moving forward, a concerted effort is essential to safeguard these fragile ecosystems and maintain the intricate web of life they support.