Unraveling Viral Ecology and Evolution Over 20 Years in a Freshwater Lake: Insights from Nature
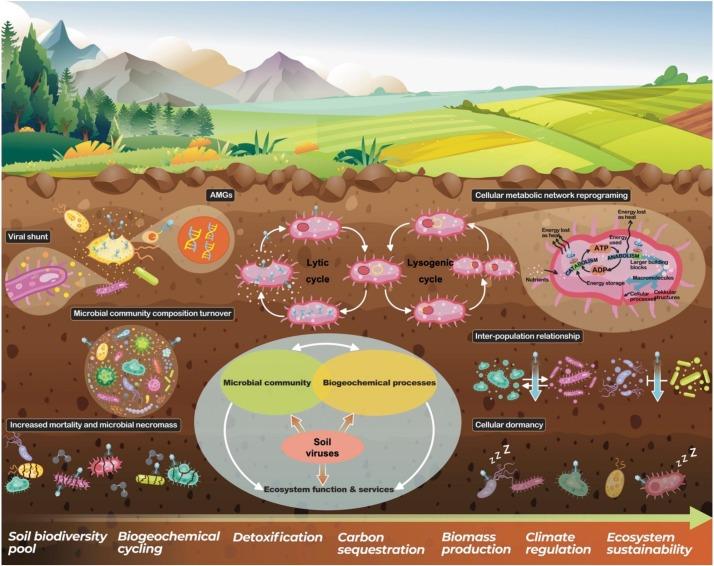
In the complex tapestry of aquatic ecosystems, viruses play a crucial yet often overlooked role in shaping microbial communities and nutrient cycling. A groundbreaking study published in Nature sheds light on two decades of research into viral ecology and evolution within a pristine freshwater lake, revealing striking patterns and profound implications for our understanding of aquatic life. As scientists analyzed vast datasets collected over 20 years, they uncovered how viral populations interact with their hosts, adapt to environmental changes, and influence the dynamics of ecosystems. This extensive investigation not only enriches our knowledge of virus-host relationships but also raises urgent questions about the impacts of climate change and human activity on freshwater ecosystems. As we delve into this comprehensive study, we explore its findings and their significance in the ever-evolving field of virology, ecology, and environmental science.
Exploring the Dynamics of Viral Diversity in Freshwater Ecosystems
The intricate interplay between viral diversity and ecosystem dynamics has garnered increasing attention in ecological studies. A recent investigation into the viral communities of a freshwater lake over the past 20 years sheds light on how environmental factors influence viral evolution and diversity. Factors such as nutrient availability, temperature fluctuations, and the introduction of invasive species significantly impact the viral populations in these ecosystems. This research highlights the adaptability of viruses, demonstrating their potential role in regulating microbial populations and influencing nutrient cycling within freshwater habitats.
Key findings from the study emphasize the following points regarding viral diversity:
- Adaptive Evolution: Viruses rapidly adapt to changing environmental conditions, showcasing high genetic variability.
- Host Interactions: The relationship between viruses and their microbial hosts is critical, influencing both viral replication and host survival.
- Ecosystem Health Indicators: Changes in viral communities can serve as indicators of ecosystem health, reflecting broader environmental changes.
To further illustrate the findings, the following table summarizes viral diversity metrics collected over two distinct periods within the study:
| Year | Diversity Index | Dominant Viral Groups |
|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 3.5 | Myoviruses, Podoviruses |
| 2023 | 4.8 | Myoviruses, Siphoviruses, Inoviruses |
Understanding the Role of Viruses in Lake Biogeochemistry
The intricate interplay between viruses and lake biogeochemistry is a fascinating area of study that has garnered significant attention in recent years. Viruses, often overlooked in aquatic ecosystems, play a crucial role in nutrient cycling, influencing the abundance and diversity of microbial communities. These microscopic agents can control populations of bacteria and phytoplankton, thereby affecting primary production and decomposition processes in freshwater environments. Their activity leads to the release of organic matter, which can be utilized by other microbial organisms, further enriching the biogeochemical landscape of the lake.
Research has demonstrated that the impact of viruses extends beyond mere population control; they also contribute to the transfer of genetic material through horizontal gene transfer, which can drive evolutionary changes in microbial populations. This dynamic interaction is particularly evident during seasonal fluctuations in lake environments, where viral abundance can peak under specific conditions. Understanding these complex dynamics is essential for deciphering the broader implications of viruses in lake nutrient cycling. Key findings include:
- Influence on nutrient availability: Viruses support the breakdown of organic material, releasing essential nutrients back into the ecosystem.
- Regulation of microbial diversity: By selectively infecting certain bacterial strains, viruses shape community compositions.
- Impact on food webs: Viruses indirectly affect higher trophic levels by regulating the populations of primary producers and consumers.
| Virus Type | Effect on Ecosystem |
|---|---|
| Infective Phage | Reduces bacterial bloom, promoting diversity. |
| Lytic Virus | Breaks down biomass, recycling nutrients. |
| Temperate Virus | Facilitates gene transfer, enhancing adaptability. |
Strategies for Monitoring and Managing Viral Populations in Aquatic Environments
Monitoring and managing viral populations in aquatic ecosystems is crucial for understanding their dynamic interactions and implications for overall ecosystem health. Effective strategies include:
- Utilizing molecular techniques: Employing high-throughput sequencing to identify viral diversity and abundance in freshwater samples.
- Longitudinal sampling: Conducting regular sampling throughout different seasons to capture temporal variations in viral populations.
- Modeling approaches: Applying ecological models to predict viral dynamics in response to environmental changes, such as temperature fluctuations and nutrient loading.
- Community engagement: Involving local stakeholders in monitoring efforts to enhance understanding and compliance with viral management strategies.
Furthermore, management practices can be bolstered by:
- Data-sharing initiatives: Establishing collaborative databases where researchers can share findings and track viral outbreaks.
- Public awareness campaigns: Educating communities about the impact of viral pathogens on aquaculture and natural water bodies to foster proactive management.
- Adaptive management frameworks: Implementing flexible management plans that can evolve based on new data and understanding of viral ecology.
| Strategy | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Molecular Techniques | Enhanced detection of viral strains |
| Longitudinal Sampling | Insights into seasonal viral trends |
| Community Engagement | Improved stakeholder involvement |
To Wrap It Up
the remarkable two-decade-long study of viral ecology and evolution in the freshwater ecosystems of Nature has illuminated the intricate dynamics that govern life in these often-overlooked environments. As researchers continue to unveil the complex interactions between viruses, their hosts, and the surrounding ecosystems, this groundbreaking work not only enriches our understanding of viral behavior but also underscores the critical role these microscopic entities play in maintaining ecological balance. As climate change and human activities continue to threaten freshwater habitats, the insights gained from this study will be invaluable for future conservation efforts and biodiversity management. By fostering a deeper appreciation for the often invisible world of viruses, scientists hope to inspire interdisciplinary approaches to safeguarding our planet’s precious freshwater resources for generations to come.