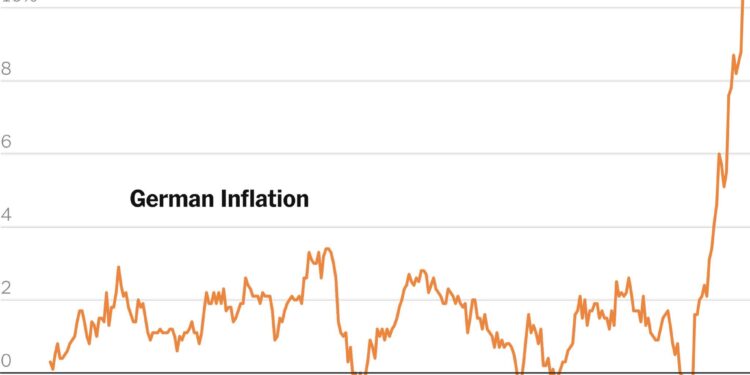
Germany’s Inflation Rate Sees Slight Decline, Raising Economic Questions
In an unexpected development, Germany’s inflation rate has decreased to 2.2% in April, a figure that does not meet the forecasts of analysts who anticipated a more pronounced drop. Recent statistics from the federal statistics office indicate that while there has been a minor easing in inflation compared to the previous month, economic pressures remain significant for both consumers and businesses. This slight reduction prompts critical inquiries regarding the future direction of Germany’s economy—the largest in Europe—as it grapples with ongoing price increases and shifting market dynamics in a post-pandemic environment. Economists and policymakers are now paying close attention to these trends as they strive for stability amid uncertainty.
Factors Affecting German Economy and Inflation Rates
The recent data reveals a modest decline in Germany’s inflation rate, currently at 2.2% for April. Although this marks an improvement over prior months, it raises concerns among economists about the robustness of economic recovery within the country. The slight decrease is largely attributed to variations in energy prices alongside changes in consumer demand, leading many experts to speculate on potential long-term ramifications for the wider European economy. Investors are closely monitoring these developments as they may impact future monetary policies, including possible interest rate changes by the European Central Bank.
- Consumer Behavior: A downturn in consumer spending could further suppress inflationary trends, indicating a potential slowdown.
- Evolving Energy Costs: Ongoing fluctuations within energy markets remain crucial when predicting future inflation rates.
- Global Economic Factors: Persistent international supply chain challenges continue to pose risks for Germany’s economic growth moving forward.
The table below illustrates month-to-month shifts in inflation rates:
| Month |
Inflation Rate (%) |
|
|
< td >April< td > 2 .0< / td >< / tr >
< / tbody >
< / table >
Effects on Consumer Spending and Business Investment Under Price Pressures
The recent revelation of slower-than-expected declines in German inflation—now at % in April—raises alarms regarding consumer behavior and business investments . As price pressures persist , consumers may alter their purchasing patterns , favoring essential items over non-essential goods . This shift could result in reduced retail sales , adversely affecting sectors such as hospitality and tourism that depend heavily on consumer confidence . Analysts are keenly observing shifts in consumer sentiment , especially since prolonged inflation can diminish purchasing power significantly .
On the corporate side , uncertainty surrounding persistent inflation might compel companies to reassess their investment strategies . Faced with rising costs , many firms may postpone or rethink expansion initiatives . Such hesitance can lead to slowed hiring processes which ultimately stifles overall economic growth . Key sectors likely impacted include :
- < strong >Manufacturing : Investment levels related to machinery upgrades might be curtailed.< / li >
- < strong >Technology : Budgets allocated towards innovation could see reductions as companies prepare for challenging times.< / li >
- < strong >Retail : Plans for expansion will likely be reconsidered due to changing consumer habits.< / li >
< / ul >
| Sector
| |
/ th >
< td Manufacturing
| < td Technology
| < td Retail
| Strategies For Managing Inflation Without Hindering Growth
The recent decline of German inflation down to % calls upon policymakers’ attention toward implementing measures aimed at effectively managing these pressures while promoting sustainable growth within economies across Europe To strike this balance, adjustments involving monetary policy should be considered; specifically through careful modulation concerning interest rates ensuring accessibility remains intact both businesses & consumers alike stimulating demand without exacerbating existing issues surrounding rising prices Furthermore enhancing supply chain efficiencies plays an integral role mitigating costs associated with inflations Investing into technology infrastructure improvements allows governments support businesses reducing operational delays stabilizing overall pricing structures.
Additionally targeted fiscal policies offer dual benefits addressing immediate concerns linked directly back towards maintaining healthy economies supporting developmental initiatives Measures like temporary tax relief directed low middle-income families help sustain purchasing power transitioning balanced budget approaches Encouraging innovation investing green technologies creates new job opportunities potentially leading reduced energy expenses long term A multifaceted approach combining monetary measures fiscal incentives technological advancements essential navigating complexities tied directly back towards managing inflations without hindering overall progress.
Conclusion: Key Insights Moving Forward
Germany’s latest reported decline brings its current standing downwards reaching %. While falling short expectations sharper decreases, ongoing challenges persist including surging energy costs supply chain disruptions influencing pricing structures As European Central Bank navigates through monetary policies responding accordingly stakeholders must remain vigilant adapting evolving market conditions ahead upcoming months prove crucial determining whether trends continue shaping Eurozone landscapes effectively.
No Result
View All Result
No Result
View All Result