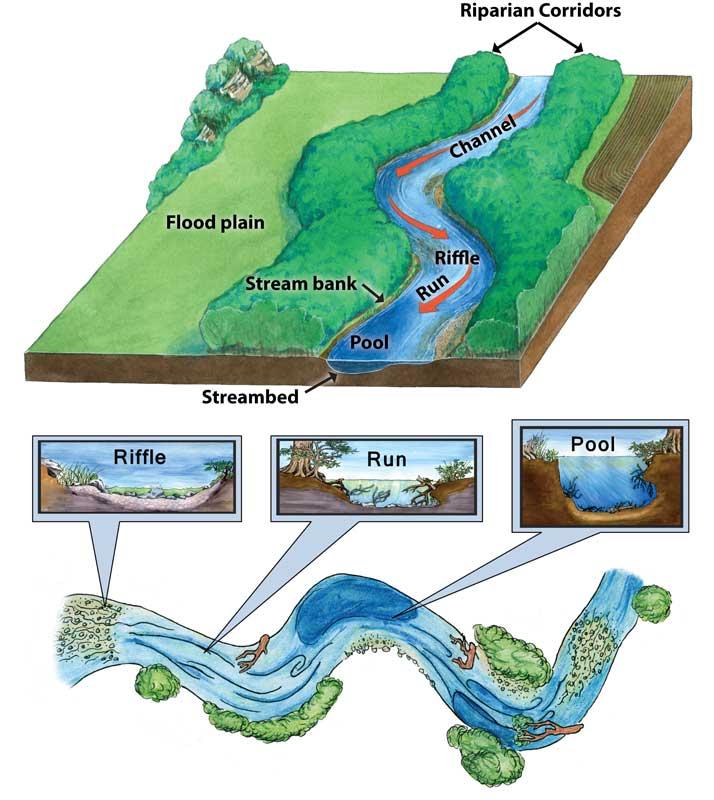
A groundbreaking new study published today has resolved a decades-old mystery in river science, shedding fresh light on the complex dynamics that govern river ecosystems. The research, featured on Cosmos Magazine, offers critical insights that could redefine how scientists understand river behavior and inform better conservation strategies worldwide. This advancement marks a significant milestone in environmental science, bridging a knowledge gap that has perplexed researchers for years.
Breakthrough Research Unveils Missing Link in River Ecosystem Dynamics
Scientists have identified a crucial mechanism that links physical river processes with the intricate web of biological interactions sustaining freshwater ecosystems. This discovery challenges previous models that underestimated the role of sediment transport and nutrient cycling in shaping aquatic biodiversity. Through advanced monitoring techniques and in-situ experimentation, researchers demonstrated how fluctuations in river flow influence habitat connectivity, directly affecting species distribution and reproductive cycles.
Key findings reveal:
- Dynamic sediment movement controls spawning grounds for fish populations.
- Variable nutrient fluxes drive the productivity of benthic microhabitats.
- Interdependent relationships between microbes and macroinvertebrates sustain food web stability.
| Factor | Impact on Ecosystem |
|---|---|
| Flow Regime | Modulates habitat connectivity |
| Sediment Transport | Shapes spawning grounds |
| Nutrient Cycling | Enhances primary productivity |
Study Reveals Critical Insights into Sediment Transport and Biodiversity Impact
The recent research offers a groundbreaking look into how sediment transport shapes river ecosystems, revealing intricate connections between physical processes and biodiversity that were previously underestimated. Scientists employed advanced monitoring techniques and high-resolution modeling to track sediment movement across varied landscapes, discovering that sediment flow not only influences river morphology but also plays a pivotal role in sustaining aquatic habitats. These findings highlight the dynamic balance required to maintain species richness, especially in regions facing intensified human intervention and climate variability.
Key outcomes of the study include:
- Identification of sediment hotspots crucial for spawning grounds of native fish species.
- Quantification of sediment input thresholds beyond which ecosystem health declines sharply.
- Analysis of sediment composition changes affecting invertebrate diversity and growth patterns.
| Parameter | Impact on Biodiversity | Measured Change |
|---|---|---|
| Fine Sediment Load | Invertebrate abundance | ↓ 30% |
| Coarse Sediment Movement | Fish spawning success | ↑ 15% |
| Total Sediment Discharge | Riparian vegetation diversity | Stable |
Experts Call for Revised River Management Policies Based on New Scientific Findings
Leading hydrologists and environmental scientists emphasize that current river management strategies often overlook critical ecosystem dynamics revealed by recent research. This new body of work shows the intricate balance between sediment flow, aquatic biodiversity, and river morphology, challenging long-standing assumptions. Experts advocate for policies that integrate adaptive management approaches, focusing on restoring natural flow regimes and accounting for seasonal variability to maintain river health and resilience against climate change.
Policy recommendations emerging from the study highlight several key actions:
- Enhancing collaboration between scientists, local communities, and policymakers.
- Implementing real-time monitoring systems to respond dynamically to ecological changes.
- Prioritizing sediment transport restoration to prevent habitat degradation.
- Incorporating indigenous knowledge into river stewardship plans for holistic outcomes.
| Parameter | Traditional Approach | New Scientific Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Management | Static seasonal releases | Dynamic seasonal variability |
| Sediment Handling | Minimal consideration | Essential for habitat health |
| Biodiversity Focus | Limited to key species | Broad ecosystem perspective |
Closing Remarks
As this groundbreaking study reshapes our understanding of river ecosystems, it not only resolves decades-old scientific debates but also opens new pathways for environmental management and conservation. With rivers playing a crucial role in sustaining biodiversity and human livelihoods, these insights arrive at a pivotal moment. Future research will build on this foundation, ensuring that the health of these vital waterways is better protected for generations to come. For more updates on developments in river science and environmental research, stay tuned to Cosmos Magazine.