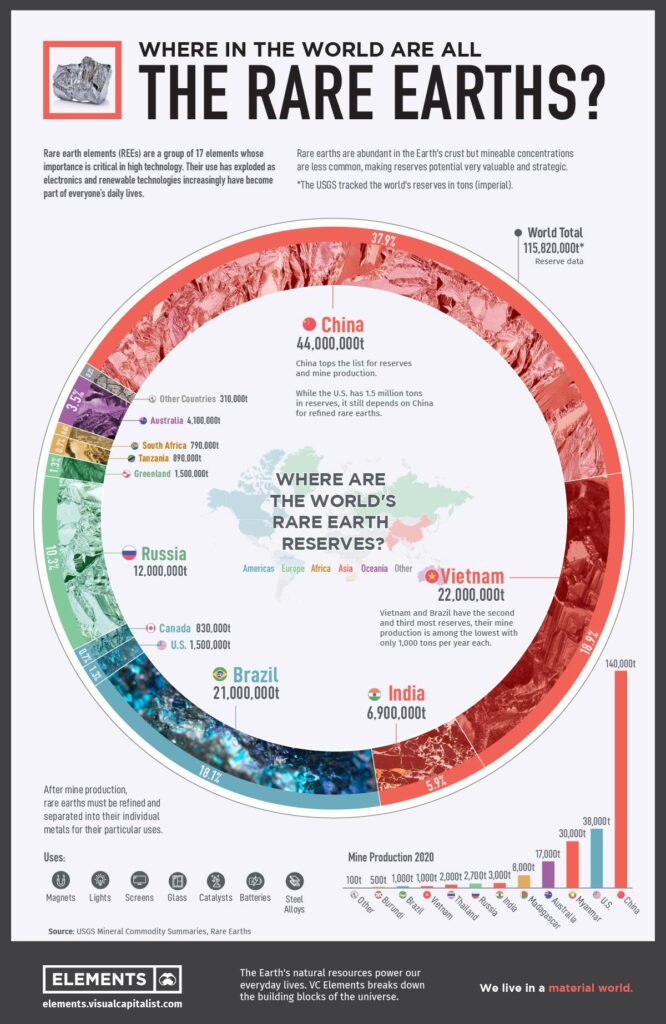
In a move that has rippled across global markets and tech industries alike, China has unveiled a fresh set of controls targeting the export of rare earth elements and advanced technologies. As the world’s dominant supplier of these critical materials, Beijing’s latest regulations signal a strategic tightening of its grip on resources essential to everything from smartphones to electric vehicles and military hardware. This development underscores the intricate balance of power in international trade and the ever-evolving landscape of technological competition, prompting governments and companies worldwide to reassess their supply chains and alliances in an era defined by geopolitical shifts and resource scarcity.
China Tightens Grip on Rare Earths and Technology Exports to Bolster Strategic Advantage
In a move signaling its intent to consolidate global influence, China has introduced a suite of stricter regulations on the export of rare earth minerals and advanced technologies. These controls are designed to ensure that critical resources and innovations remain under tight government oversight, potentially reshaping global supply chains and technological development trajectories. The restrictions particularly target industries linked to electronics, defense, and renewable energy sectors, emphasizing the nation’s commitment to leverage its rich reserves and manufacturing capabilities as strategic assets.
Key aspects of these new controls include:
- Expanded licensing requirements for rare earth material shipments
- Enhanced vetting processes for technology exports to foreign entities
- Limits on quantities and frequencies of export approvals
- Closer monitoring of downstream applications involving sensitive tech
| Resource/Tech Type | Export Restriction Level | Target Sectors |
|---|---|---|
| Neodymium & Dysprosium | High | Electric Vehicles, Aerospace |
| Advanced Semiconductors | Moderate | Consumer Electronics |
| Quantum Computing Components | Strict | |
| Quantum Computing Components | Strict | Defense, Research Institutions |
| Lithium & Cobalt | Moderate | Renewable Energy, EV Batteries |
These measures reflect China’s strategic approach in safeguarding its technological edge and resource wealth amid intensifying global competition. Observers anticipate that such export controls could prompt multinational companies to reassess supply chain dependencies and accelerate diversification efforts.
If you’d like, I can help you further refine or expand this content!
Implications for Global Supply Chains and Industry Stakeholders
Heightened restrictions on rare earths and technology exports by China are poised to disrupt global supply chains significantly. Key industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, and defense, may face increased lead times and rising costs as alternative sources or suppliers are sought. This strategic move underscores China’s intent to exert greater influence over critical materials essential for modern manufacturing, compelling businesses to reassess risk management strategies and diversify procurement channels with urgency.
Industry stakeholders must now consider several evolving factors:
- Supply chain resilience: Investing in stockpiles and localizing rare earth processing facilities.
- Geopolitical dynamics: Navigating trade tensions that may affect collaboration and technology transfers.
- Innovation push: Accelerating research into alternative materials and recycling methods.
| Stakeholder | Primary Concern | Strategic Response | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturers | Raw material scarcity | Diversifying supplier base | |||||||||
| Investors | Market volatility | Monitoring geopolitical shifts | |||||||||
| Governments | Supply security |
Impact of China’s Heightened Restrictions on Rare Earths and Technology ExportsHeightened restrictions on rare earths and technology exports by China are poised to disrupt global supply chains significantly. Key industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, and defense, may face increased lead times and rising costs as alternative sources or suppliers are sought. This strategic move underscores China’s intent to exert greater influence over critical materials essential for modern manufacturing, compelling businesses to reassess risk management strategies and diversify procurement channels with urgency. Industry stakeholders must now consider several evolving factors:
Stakeholder Table| Stakeholder | Primary Concern | Strategic Response | If you want, I can assist in expanding on the impacts or strategies for any specific stakeholder group or help analyze potential market implications. Let me know how you’d like to proceed! Navigating the New Export Landscape Recommendations for Businesses and PolicymakersAmid tightening regulations, businesses must refine their strategic approach to maintaining supply chain resiliency and market access. Diversification of sourcing has moved from a luxury to a necessity; companies should actively explore alternative suppliers beyond traditional hubs, especially for rare earth elements and advanced technologies. Leveraging innovation in material science to reduce dependency on constrained resources can provide a competitive edge. Additionally, embracing transparent compliance programs will mitigate risks posed by evolving export controls and help cultivate stronger trust with international partners. Policymakers, on the other hand, face the delicate task of balancing national security interests with the needs of global trade. It is critical to foster dialogue between government bodies and industry stakeholders to craft flexible frameworks that anticipate market shifts without stifling innovation. Implementing targeted support such as:
can alleviate tensions and promote a stable export environment. The table below highlights key focus areas for both sectors in navigating this new export terrain:
Closing RemarksAs China moves to tighten its grip on the export of rare earth elements and critical technologies, the global supply chains and markets stand at a crossroads. This new chapter in trade controls not only signals Beijing’s strategic priorities but also challenges countries and industries to rethink their dependencies and innovation pathways. As the world watches closely, the ripple effects of these policies will unfold-reshaping alliances, technological advancement, and the future landscape of global commerce. |