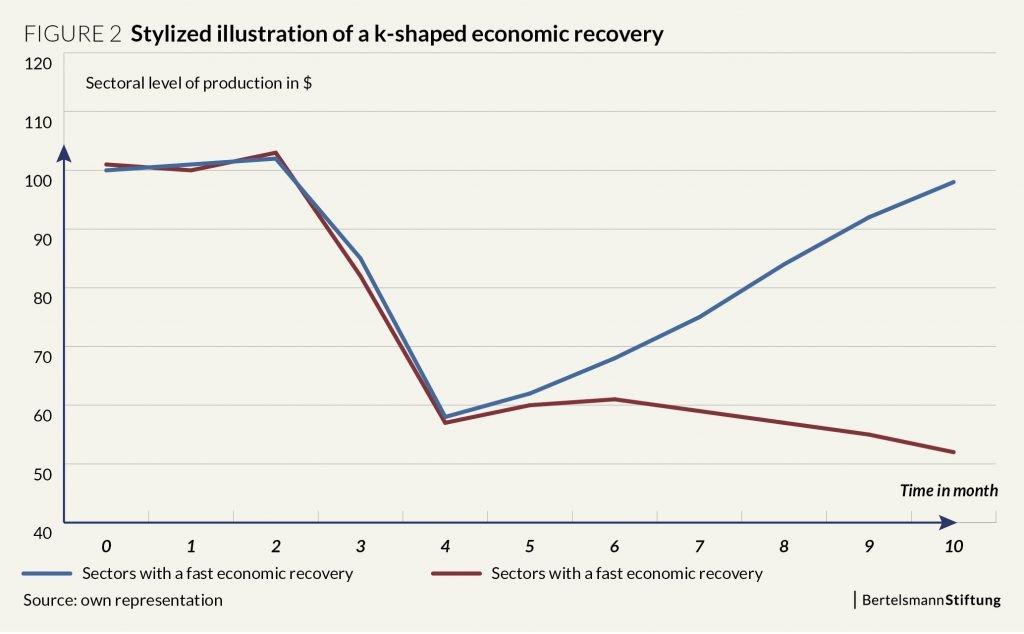
As the U.S. economy grapples with uneven recovery patterns, concerns are mounting over the emergence of a potentially K-shaped rebound-where sectors and demographics diverge sharply in economic fortunes. This growing disparity presents a complex challenge for the Federal Reserve as it navigates monetary policy decisions aimed at fostering broad-based growth while mitigating inflation risks. In an exclusive report, The Hill examines how this bifurcated economic landscape complicates the Fed’s strategy and raises questions about the path forward amid a deeply divided recovery.
K-shaped Economic Recovery Deepens Wealth and Employment Divides
Economic divergence continues to deepen as key sectors and demographics rebound unevenly from the pandemic-induced downturn. High-income households and industries tied to technology and finance have swiftly regained ground, with soaring asset prices and robust hiring. Meanwhile, many lower-wage workers, particularly in retail, hospitality, and service sectors, face stagnant wages, job insecurity, and slow employment growth. This uneven trajectory has intensified concerns about systemic inequalities, fueling debates on how monetary policy can address disparate recovery paths without exacerbating inflationary pressures.
Policymakers are grappling with the unintended consequences of supporting a bifurcated economy. While aggressive stimulus and low interest rates have buoyed wealthier segments, relief has barely reached those most vulnerable. The Fed’s challenge lies in balancing economic stability against widening disparities, as reflected in the following indicators:
- Asset appreciation: Stock indices and real estate markets have surged, benefiting affluent investors.
- Employment gains: Predominantly concentrated in high-skill sectors with remote work flexibility.
- Wage stagnation: Persisting among frontline and low-income workers.
| Sector | Job Recovery Rate | Average Wage Change |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | +12% | +5.3% |
| Hospitality | +3% | +0.8% |
| Retail | +4% | +1.2% |
| Finance | +10% | +4.7% |
Federal Reserve Faces Balancing Act Between Inflation Control and Growth Support
The Federal Reserve finds itself navigating a complex economic landscape marked by uneven recovery patterns across different sectors and demographics. While inflation remains elevated, fueled predominantly by supply chain disruptions and rising energy costs, growth indicators are showing signs of vulnerability in lower-income communities. This divergence creates tension in monetary policy decisions, as tightening measures to curb inflation could inadvertently suppress economic opportunities for those still lagging behind.
- Inflation pressures: Persistently high consumer prices, especially in housing and food.
- Growth disparities: Job gains concentrated in high-wage industries, while service and retail sectors struggle.
- Monetary policy dilemma: Raising interest rates risks widening the economic gap, yet delayed action may fuel further inflation.
| Economic Indicator | Trend | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Price Index (CPI) | Up 6.5% YoY | Higher cost of living |
| Unemployment Rate | Down to 3.7% | Improvement in labor market |
| Wage Growth | Strong in tech, weak in retail | Income inequality persists |
Policy Recommendations Urge Targeted Interventions to Address Economic Inequities
In light of growing economic disparities, policymakers are advocating for targeted strategies that specifically address the widening wealth and income gaps. These interventions prioritize bolstering support for vulnerable communities through enhanced social safety nets, affordable housing initiatives, and expanded access to quality education and healthcare. By focusing resources on those most impacted by economic shifts, the goal is to counteract the divergent recovery trends evident in a bifurcated economy. Experts warn that a generic, one-size-fits-all approach could exacerbate inequities and stall broader economic progress.
Among the proposed measures, several stand out for their potential immediate impact:
- Targeted fiscal stimulus to support low-income households and small businesses
- Expanded job training programs aimed at workers displaced by technological change
- Increased investment in community infrastructure to stimulate local economies
- Strengthened wage policies that promote equitable income growth
| Intervention | Expected Outcome | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Income Support Programs | Reduce poverty rates | ||||||||
| Job Retraining | Increase workforce adaptability | ||||||||
| Affordable Housing Initiatives | Improve housing stability | ||||||||
| Community Investment |
In light of growing economic disparities, policymakers are advocating for targeted strategies that specifically address the widening wealth and income gaps. These interventions prioritize bolstering support for vulnerable communities through enhanced social safety nets, affordable housing initiatives, and expanded access to quality education and healthcare. By focusing resources on those most impacted by economic shifts, the goal is to counteract the divergent recovery trends evident in a bifurcated economy. Experts warn that a generic, one-size-fits-all approach could exacerbate inequities and stall broader economic progress. Among the proposed measures, several stand out for their potential immediate impact:
|