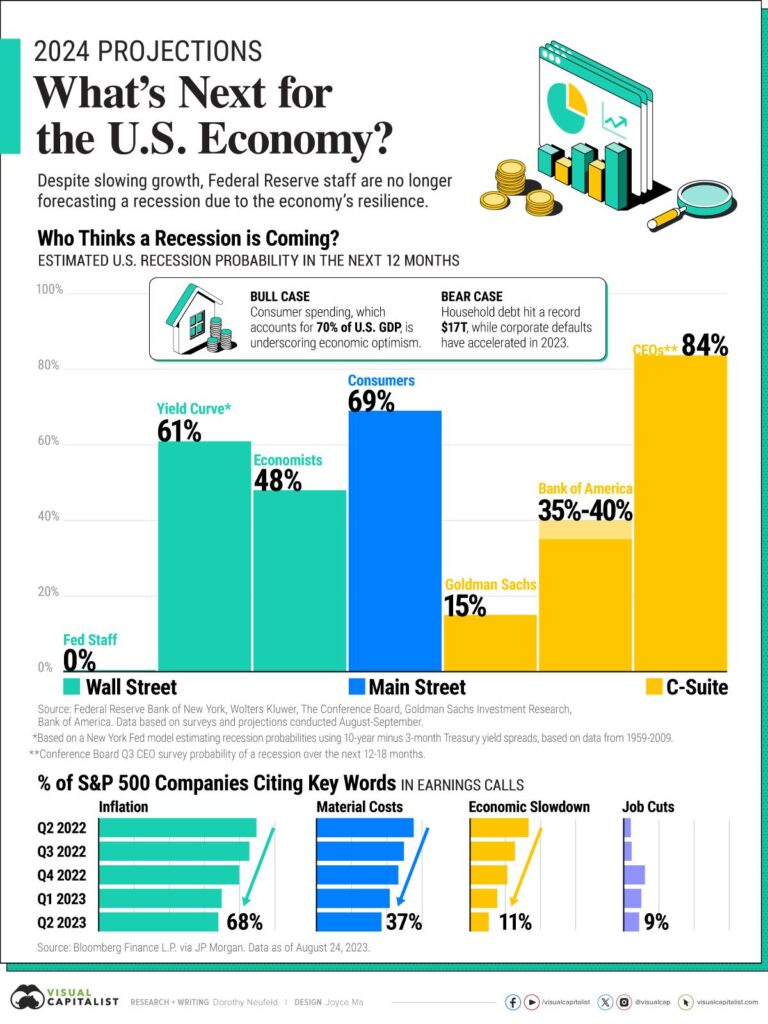
The US economy shows signs of resilience and steady growth, with strong employment numbers and robust consumer spending underpinning a positive outlook. However, amid these encouraging indicators, concerns loom over the Federal Reserve’s recent policy decisions and outlook. While the broader economy appears to be in a good place, the central bank’s cautious stance and persistent inflation challenges suggest a more complicated path ahead for monetary policy, raising questions about how the Fed will navigate the evolving economic landscape.
US Economy Shows Resilience Amid Global Challenges
The US economy continues to demonstrate remarkable strength despite ongoing global uncertainties, including supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions. Key indicators such as consumer spending, employment rates, and industrial output have remained robust, reflecting an underlying resilience that defies many forecasters’ earlier projections. Businesses across sectors are adapting swiftly to changing demands, supported by sustained consumer confidence and a recovering labor market. Experts highlight that while inflationary pressures persist, they have begun to moderate, allowing for cautious optimism among market watchers.
Meanwhile, the Federal Reserve faces a delicate balancing act as it navigates the conflicting priorities of curbing inflation without stifling growth. Recent policy discussions have underscored the challenge of tightening monetary policy amid a resilient but still vulnerable economy. Below is a summary of key economic indicators and recent Fed actions:
| Indicator | Current Status | Fed Response |
|---|---|---|
| Inflation Rate | 5.1% (slightly down) | Interest rate hikes |
| Unemployment Rate | 3.6% (near historic lows) | Monitored closely |
| Consumer Spending | Steady growth | Supportive monetary stance |
- Supply chain resilience has improved, easing cost pressures.
- Business investments are cautiously rising, signaling confidence.
- Wage growth remains moderate, curbing overheating risks.
- Federal Reserve policies are under intense scrutiny for balancing risk.
Federal Reserve Faces Pressure as Inflation Risks Persist
The Federal Reserve finds itself navigating a complex economic landscape as inflationary pressures continue to challenge policymakers. Despite encouraging signs of sustained growth and resilience in the labor market, inflation remains stubbornly above the central bank’s 2% target. This persistent upward trend in consumer prices has intensified debates within the Fed, with some officials advocating for a more aggressive tightening of monetary policy while others caution against stifling the ongoing economic recovery.
Market watchers are carefully monitoring key indicators that highlight inflation dynamics. Factors such as rising commodity prices, supply chain bottlenecks, and strong consumer demand contribute to an uncertain outlook. The tensions have led to a cautious approach, weighing the risks of overheating against the potential fallout of rapid rate hikes. Below is a snapshot of recent inflation-related data:
| Indicator | Recent Value | Change (Year-over-Year) |
|---|---|---|
| CPI (Consumer Price Index) | 5.3% | +0.2% |
| Producer Price Index | 6.1% | +0.4% |
| Core Inflation Rate | 4.7% | +0.3% |
- Supply chain disruptions continue to push prices higher in several sectors.
- Wages have increased, adding to the inflationary wage-price spiral concerns.
- Commodity costs like oil and metals remain volatile, contributing to uncertainty.
Experts Recommend Strategic Policy Adjustments to Sustain Growth
Leading economists emphasize the need for a measured approach in tailoring monetary and fiscal policies to ensure long-term economic stability. While consumer spending and job growth remain robust, experts warn that complacency could lead to overheating or inflationary pressures. Key recommendations include:
- Gradual interest rate adjustments that respond to inflation data without stifling growth.
- Targeted fiscal stimulus to support emerging sectors such as green energy and technology innovation.
- Enhanced regulatory oversight to curb speculative risks within financial markets.
A recent analysis outlines how synchronized policy shifts can enhance resilience. The table below summarizes proposed policy levers and their anticipated impact over the next 12 months:
| Policy Lever | Expected Outcome | Implementation Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Incremental Rate Hikes | Moderate inflation without dampening hiring | 3-6 months |
| Targeted Tax Incentives | Boost investments in innovation sectors | 6-9 months |
| Stronger Market Oversight | Prevent asset bubbles | Ongoing |
In Summary
As the US economy shows resilience with steady growth and low unemployment, the Federal Reserve faces mounting challenges in balancing inflation concerns and monetary policy adjustments. While economic indicators paint a generally positive picture, the path ahead remains uncertain as policymakers navigate complex dynamics to sustain this momentum without triggering new risks. The coming months will be critical in determining whether the Fed can steer the economy through these pressures while maintaining stability.