Forecasting Economic Impacts of Invasive Species: A Novel Analytical Framework
In the intricate intersection of ecology and economics, grasping the financial ramifications of invasive species has emerged as a critical issue for both researchers and policymakers. A pioneering study recently featured in the esteemed journal Nature illuminates methods to anticipate the costs linked to biological invasions, even when faced with limited data. This cutting-edge approach merges sophisticated statistical techniques with ecological knowledge, providing an essential resource for addressing the economic and environmental challenges posed by non-native species. As global trade dynamics and climate change heighten invasion risks, these findings could be pivotal in shaping effective management strategies across various ecosystems. In a time where financial resources are increasingly scrutinized, enhancing our ability to predict costs from minimal data not only deepens our comprehension of ecological interactions but also lays groundwork for more strategic decision-making in conservation initiatives.
Analyzing Invasion Costs with Data Modeling Methodologies
As ecosystems confront threats from invasive species, it is vital to thoroughly assess the associated economic impacts. By utilizing advanced data modeling methodologies, researchers can create predictive analytics that estimate the financial burden imposed by these invaders. Given that comprehensive datasets are often lacking, innovative approaches employing machine learning alongside statistical analysis can bridge these gaps—allowing stakeholders to pinpoint high-risk regions and allocate resources more effectively. Several key elements influencing invasion-related costs include:
- Ecological Consequences: Alterations in native biodiversity and ecosystem functions.
- Economic Disruption: Financial implications affecting agriculture and fisheries.
- Management Costs: Investments required for control measures.
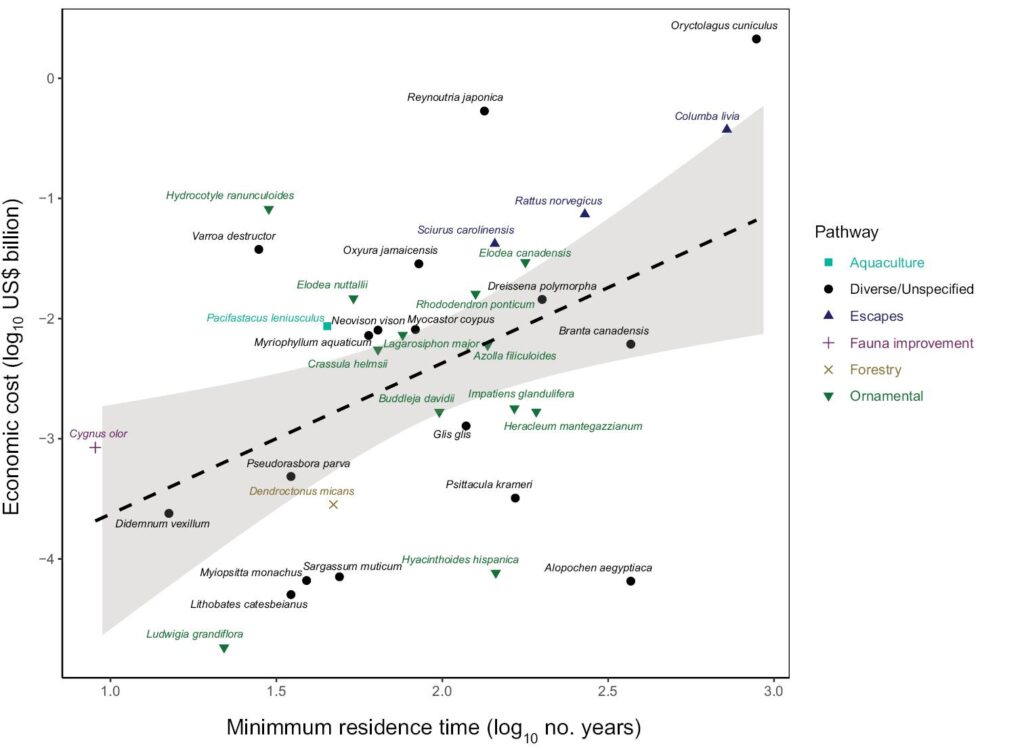
Additionally, case studies indicate that valuable insights can be derived from seemingly unrelated datasets which enhance predictive accuracy. For instance, a recent examination highlighted how variations in local economies coupled with species distribution trends are crucial for making reliable forecasts. Below is a summary table showcasing significant findings:
| Region |
Pest Species |
Total Estimated Cost ($ million) |
Affected Sector |
| The Great Lakes Region |
Zebra Mussels |
$500 million |
Aquatic Infrastructure |
The United States Nationwide
|
Asian Carp
td >< td >$200 million
td >< td >Fishing Industry
td > tr >< tr >< td >Australia
td >< td >Cane Toads
td >< td >$150 million
| Biodiversity Decrease
| tr >
< / tbody >
< / table >
Utilizing Limited Datasets for Precise Economic Forecasting
The increasing frequency of invasions poses significant challenges as economies strive to manage resource disruptions; thus leveraging limited datasets presents an exceptional opportunity to improve forecasting accuracy. Effectively using available information—even when incomplete—demands innovative methodologies capable of filtering out irrelevant noise while extracting meaningful signals. Analysts might apply techniques such asandto uncover patterns or correlations that may not be immediately visible; this transforms sparse data into robust economic predictions.
- < strong >Enhanced Predictive Capabilities< / strong >/ li >
- < strong >Cost-effective Strategies< / strong >/ li >
- < strong >Data-driven Decision Making< / strong >/ li >
< / ul >
Additionally , establishing frameworks that integrate sparse datasets can yield deeper insights into macroeconomic trends influenced by external factors like geopolitical events or climate changes . By combining diverse sources such as historical records , expert evaluations ,and real-time analytics , economists gain a holistic view . For example , consider this table illustrating connections between invasion incidents and their economic repercussions : p >
| Invasion Incident
| |
Total Estimated Economic Impact ($ Billion)< th />
| | Data Sources<
/ th > tr > head >
tr >
tr >
tr >
This analytical framework built on limited datasets is essential for navigating uncertainties inherent in predicting economic impacts related to invasions . As scholars continue exploring these avenues,the implications on policy-making could lead transformative changes .
Reducing Financial Risks: Strategic Guidelines for Stakeholders
As predicting costs associated with invasions becomes increasingly challenging due to limited information available stakeholders must adopt proactive measures aimed at minimizing their financial exposure . ImplementingDiverse Investment Strategies,for instance,could serve as protection against unforeseen expenses arising from ecological disturbances.This involves distributing funds across various sectors including technology agriculture,and environmental preservation which provides alternative options.Additionally fostering collaboration among local governments,research institutions,and other stakeholders yields invaluable insights enabling informed decisions based on emerging trends.
Furthermore adoptingPioneering Predictive Analytics,equipped with machine learning capabilities,gives stakeholders substantial advantages through generating accurate forecasts despite minimal input.A collaborative effort involving cross-sectoral data sharing significantly enhances model outputs.The following table outlines key recommendations stakeholders should consider:
|
th /> th> head >
| Diverse Investment Strategy
<< Reduces reliance on single sector
<< b>Cohesion With Researchers
<< Accesses critical insights
<< b>Pioneering Predictive Analytics
<< Enhances forecast precision
<< b>Cyclical Risk Assessment
<< Ongoing identification potential threats
Conclusion
The research published within Nature highlights an essential yet complex aspect concerning environmental science: estimating economic consequences stemming from biological invasions amidst scarce information.By integrating innovative modeling strategies alongside restricted datasets,researchers have paved pathways toward improved forecasting capabilities informing policy decisions regarding conservation efforts.As invasive organisms persistently jeopardize both ecosystems & economies alike,the revelations drawn from this study hold unprecedented significance.Policymakers & conservationists must heed these findings utilizing them effectively bolster prevention tactics while managing resources judiciously.Incorporating advanced analytical tools into ecological investigations signifies remarkable progress promising enhanced readiness against fiscal burdens resulting due ongoing shifts within our environment.As we navigate through intricacies surrounding biodiversity decline,this research serves reminder emphasizing importance informed actions grounded scientific understanding paving way towards resilient future.
|