10. Earth’s Mauna Kea

NASA
Earth’s tallest mountain, Mauna Kea, from base to tip stands 33,500 feet tall—more than a mile taller than Everest.
Mauna Kea is located on the Big Island in Hawaii and is a sacred location that holds significant cultural significance to native Hawaiians. Its snowy peak is capped with a suite of observatories that help astronomers peer across the universe.
9. Venus’ Maat Mons

NASA/JPL
Maat Mons is Venus’s tallest volcano. This radar image of the volcano was taken in 1991 by NASA’s Magellan spacecraft. Covered in patches of dark lava, the roughly four-mile-high shield volcano certainly stands out on the piping hot planet.
The volcano gets its name, Maat, from the Egyptian goddess of truth, justice, and harmony and Mons for the latin word for mountain.
8. Enceladus’ Cryovolcanoes

NASA/JPL-Caltech/SSI/PSI
You read that right. Ice volcanoes. These frozen features across the surface of Saturn’s moon, Enceladus, have tantalized scientists since their icy plumes were first spotted in 2005. Cryovolcanoes on Enceladus’s surface are thought to spray jets of water vapor, ice, and a mysterious mixture of gases into space.
Enceladus is also very tiny. The moon has a diameter of approximately 310 miles across. It’s smaller than Olympus Mons, speaking of which…
Advertisement – Continue Reading Below
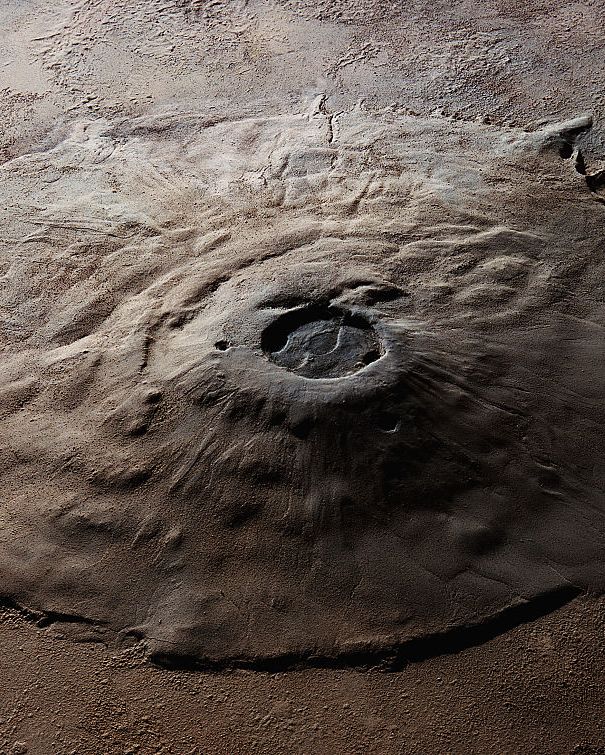
7. Mars’ Olympus Mons

Historical//Getty Images
Mars’ Olympus Mons is the largest volcano in the solar system. It’s approximately 374 miles across (roughly the size of Arizona), 16 miles tall, and has a 50-mile-wide crater at its summit.
Lava flows stretch further on Mars thanks to the lower surface gravity and high eruption frequency. Scientists believe the volcano has been dormant for at least 2 million years because there isn’t evidence of recent volcanic lava nearby.
6. Triton’s Active Cryovolcanoes
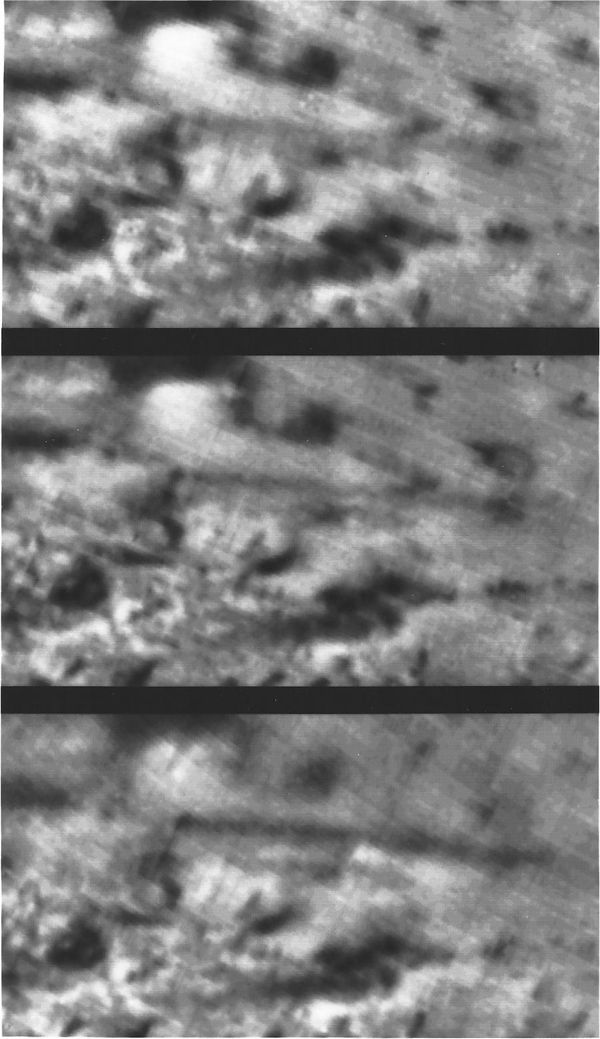
NASA/JPL
These pixelated images each taken 45 minutes by Voyager 2 in 1989 shows the five-mile-high plume of an active cryovolcano on Neptune’s moon Triton.
At the time, scientists suspect that the large, dark cloud of particles likely contained frozen nitrogen and methane, according to the Chicago Tribune. Still, researchers are puzzling over the peculiar moon, even as recent technology has allowed them to analyze the imagery in even greater detail.
5. Mars’ Tharsis Montes

NASA/JPL/USGS
Mars’ largest volcanic region consists of not one, not two, but three separate volcanoes strung along the surface of the red planet. Tharsis Montes is composed of three dormant shield volcanoes called Arsia, Pavonis, and Ascraeus Mons, each of which are 220 to 250 miles in diameter and roughly 44 miles apart.
This image, taken by NASA’s Viking orbiter, was released in 1998 and also shows Mars’ largest single volcano, Olympus Mons, in the upper left corner.)
Advertisement – Continue Reading Below
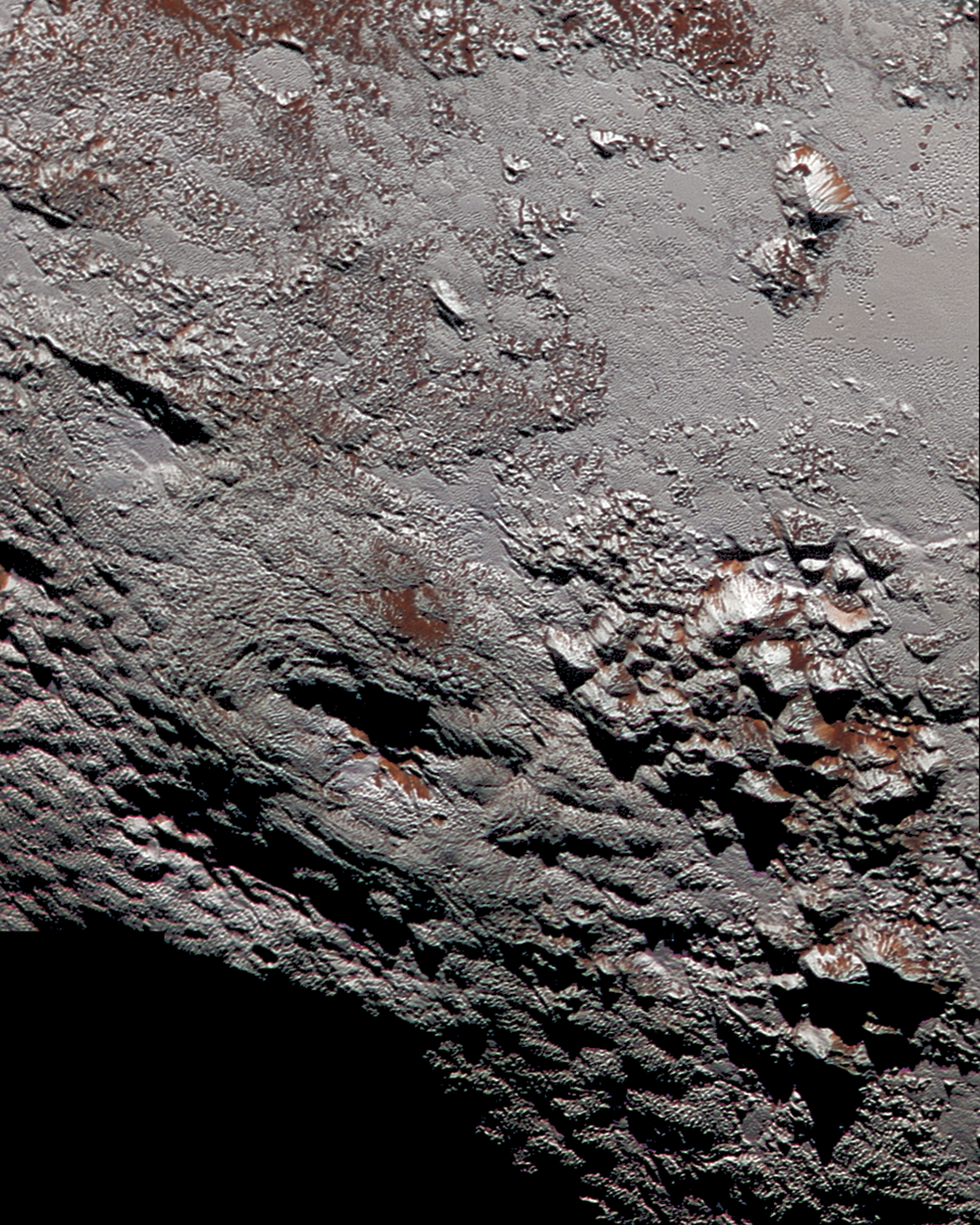
4. Pluto’s Wright Mons

NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI
Ever since NASA’s New Horizon’s spacecraft zipped past Pluto in 2015, scientists have been feverishly analyzing imagery of the dwarf planet.
Though it has yet to be confirmed, many scientists believe this image of a 90-mile-wide feature taken in Pluto’s southern hemisphere could be evidence of cryovolcanism on the former planet. If so, this feature—dubbed Wright Mons after the famous flyers—would be the largest known volcano in the outer solar system.
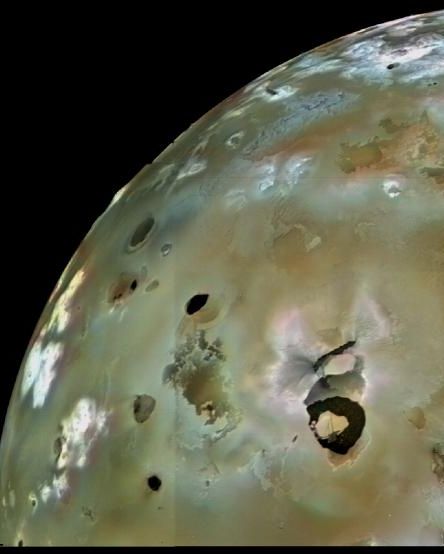
3. Io’s Loki Patera

NASA/JPL/USGS
Loki Patera is an active lava lake on the surface of Jupiter’s moon, Io. It was first spotted by Voyager 1 in 1979, and has been captivating scientists ever since.
The 125-mile-wide Loki Patera erupts in regular intervals, approximately every 540 Earth days. Its last eruption was in May 2018, so scientists predict the next eruption should be on its way.
2. Venus’ Pancake Volcanoes
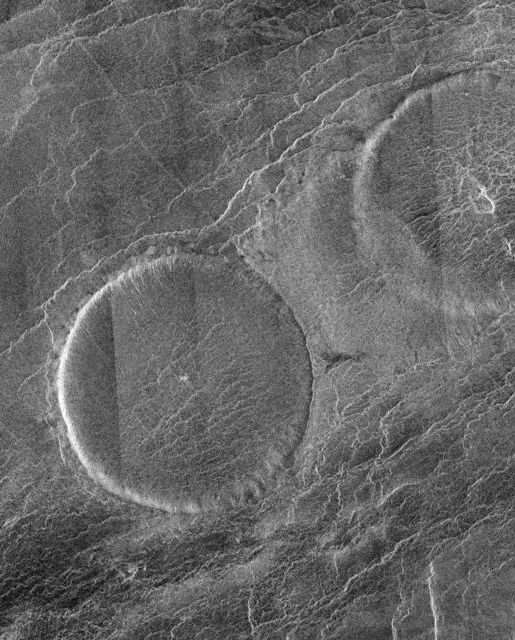
NASA/JPL
Feeling hungry?
Venus’s pancake volcanoes are among the strangest features in the solar system. Pancake dome volcanoes are named after the beloved breakfast food because of their flat, circular shape. The viscosity (stickiness) and weight of their lava flows are thought to give them this strange shape. The domes in this image are roughly 40 miles wide.
This particular group of Venusian pancake volcanoes is named Carmenta Farra and was imaged by NASA’s Magellan spacecraft in 1991.
Advertisement – Continue Reading Below
1. Titan’s Doom Mons
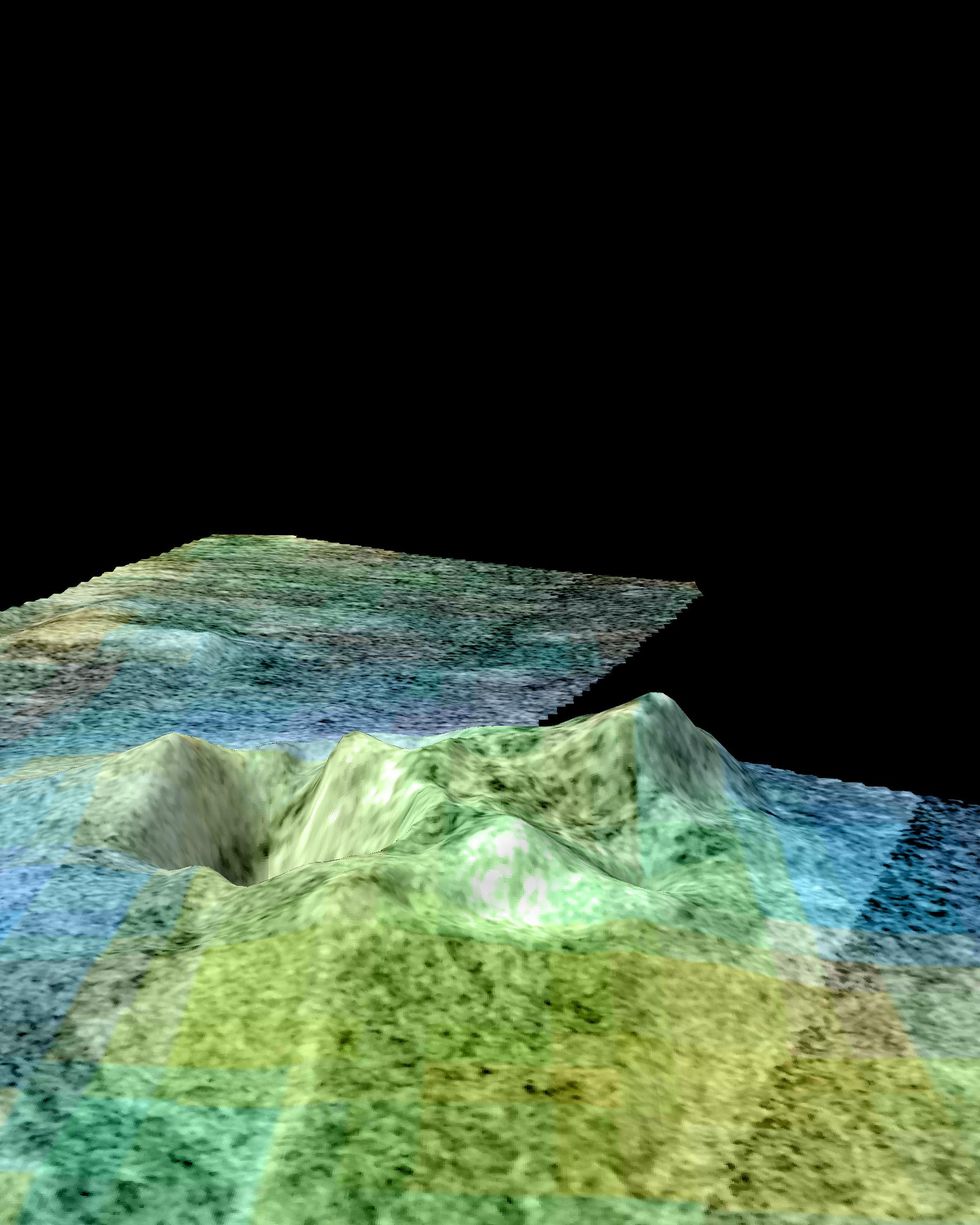
NASA/JPL-Caltech/USGS/University of Arizona
With a name like Doom Mons, how could it not be the solar system’s most fascinating feature?
Doom Mons is possibly the highest peak (and belongs to the largest mountain range) on Saturn’s moon, Titan. It’s large, too, with a diameter almost 45 miles wide. Curiously, it sits right next to Sotra Patera, the deepest depression yet found on the moon. Planetary volcanologists suspect that Doom Mons, and the nearby Erebor Mons, are cryovolcanoes which erupt water melted deep below the surface.
Jennifer Leman
Jennifer Leman is a science journalist and news editor at Popular Mechanics, where she writes and edits stories about science and space. A graduate of the Science Communication Program at UC Santa Cruz, her work has appeared in The Atlantic, Scientific American, Science News and Nature. Her favorite stories illuminate Earth’s many wonders and hazards.
>>> Read full article>>>
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source : Men’s Health – https://www.menshealth.com/trending-news/g46244481/best-volcanoes/










