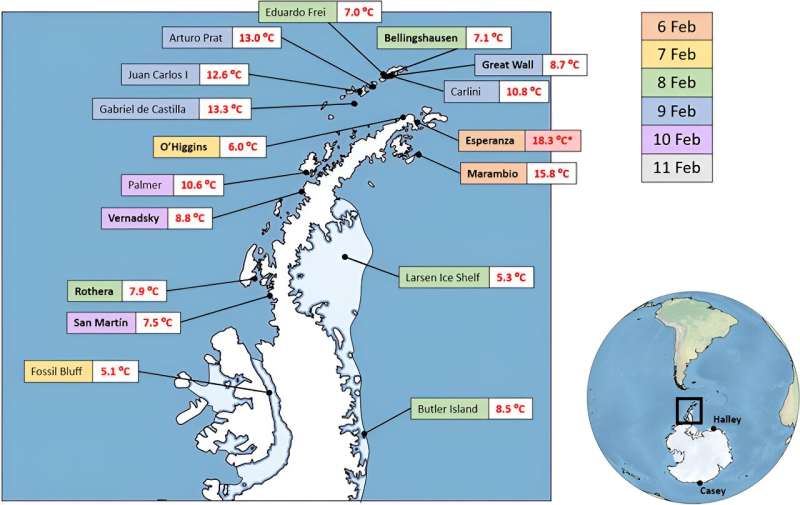
Record-breaking temperatures during the heatwave on 6 February 2020. Credit: González-Herrero et al. (2022)
In recent years, Antarctica has experienced a series of unprecedented heat waves. On 6 February 2020, temperatures of 18.3°C were recorded, the highest ever seen on the continent, beating the previous record of 17.5°C which had only been set a few years earlier.
Around February 2022, another strong heat wave in Antarctica led to record-breaking surface ice melt. In March of the same year, East Antarctica saw its strongest ever heat wave, with temperatures soaring to 30°C or 40°C higher than the average in some areas.
Over the last year, we have seen the lowest levels of Antarctic sea ice coverage since records began.
Events in recent years have bordered on the unbelievable, and it is difficult not to link them to climate change. In fact, studies have already emerged that clearly attribute some of these heat waves to global warming: one of our investigations strongly suggests that without the influence of climate change, 2020’s record-breaking temperatures would not have occurred.
Antarctica’s changing climate
In 2009, a study quantified the speed of ecosystem migration due to climate change on a global scale, and documented, essentially, the speed at which certain species have to move to ensure their survival. It concluded that biomes were moving at a speed between 0.8 km and 12.6 km per decade, with an average speed of 4.2 km per decade.
In our more recent study, published in February 2024, we adapted this measurement of speed and applied it to the edges of Antarctica. To do this, we tracked the southward migration of the zero-degree isotherm.
Evolution of the annual and seasonal position of the zero-degree isotherm in Antarctica between 1957 and 2020. The initials indicate the seasons for each measurement. MAM: autumn, JJA: winter, SON: spring, DJF: summer. Credit: González-Herrero et al. (2024)
The zero-degree isotherm is an imaginary line that encloses the areas that are at zero degrees or lower. Its southward movement means that the area with temperatures below zero Celsius in Antarctica is getting smaller and smaller. Given that water freezes at zero degrees, this movement will have serious consequences for ecosystems and for the cryosphere (areas of the Earth where water is frozen).
Our calculations show that the zero-degree isotherm has moved at a speed of 15.8 km per decade since 1957 in the area surrounding the Antarctic, while on the Antarctic peninsula itself it has moved at 23.9 km per decade. As a result, it now sits more than 100 km south of where it was in the mid 20th century.
These measurements show that the speed of climate change on the edge of Antarctica is four times faster than the average of other ecosystems.
The effects of emissions
To predict the consequences of the southward migration of the zero-degree isotherm, we ran our data through twenty different climate models. Although there is some variation in the shift of the isotherm among the models, all agree that it will move significantly further southward over the next few decades.
The models also predict that, over the coming decades, the isotherm’s movement will accelerate regardless of emissions. However, the extent of its southward movement in the second half of the 21st century will depend on how much carbon we emit.
If we continue at our current rate of emissions, the zero-degree isotherm will continue to advance at a similar rate before slowing down during the second half of the 21st century. However, if emissions are higher, the isotherm’s migration will accelerate continuing its southward movement until the end of the century.
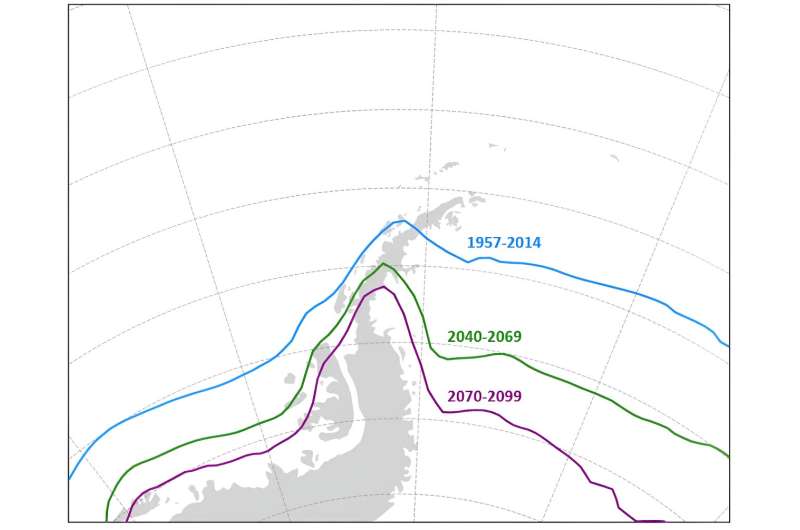
Change in the summertime position of the zero-degree isotherm over the course of the 21st century. Based on IPCC climate scenario SSP5-8.5, whereby current emission levels are approximately doubled by 2050. Credit: Adapted by González-Herrero et al. (2024)
Impacts on the cryoshpere and ecosystems
The zero-degree isotherm’s southward movement will not remain solely in the atmosphere, it will also affect the cryosphere (all of the frozen areas of Antarctica) and the biosphere (the species that live there).
Changes in the isotherm’s position will mean more liquid rain instead of snow in the outermost regions of the continent, though it may in fact cause increased snowfall in other areas.
Reduced snowfall on the frozen sea—which acts as insulation—may lead to accelerated loss of sea ice during summer thaw periods.
Although the effects on permafrost, ice shelves and continental ice are still uncertain, it will undoubtedly affect the peripheral glaciers of the Antarctic Peninsula. These constitute one of the largest potential sources of sea level rise in the coming decades.
Changes in the cryosphere will also lead to changes in ecosystems. New areas will become habitable thanks to thawing ice, but with more areas above zero degrees, invasive species from warmer, more hospitable continents may be able to settle, and they will compete with native species for resources.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()
Citation:
Climate change is speeding up in Antarctica (2024, March 19)
retrieved 19 March 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-03-climate-antarctica.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
>>> Read full article>>>
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source : Phys.org – https://phys.org/news/2024-03-climate-antarctica.html










