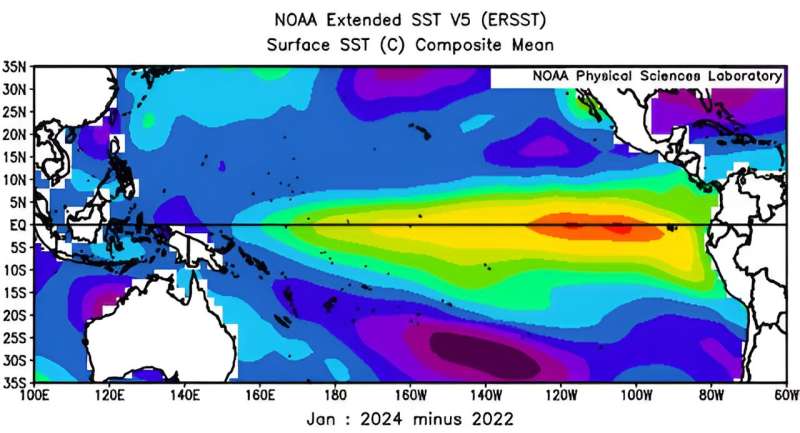
Reds and yellows show where Pacific waters were warmer in 2024 than in 2022. The abnormally warmer region along the equator is what we call El Niño. Weak El Niño events occur every few years, with strong events like this averaging once every 10 to 20 years. Credit: NOAA
Wild weather has been roiling North America for the past few months, thanks in part to a strong El Niño that sent temperatures surging in 2023. The climate phenomenon fed atmospheric rivers drenching the West Coast and contributed to summer’s extreme heat in the South and Midwest and fall’s wet storms across the East.
That strong El Niño is now starting to weaken and will likely be gone by late spring 2024.
So, what does that mean for the months ahead—and for the 2024 hurricane season?
What is El Niño?
Let’s start with a quick look at what an El Niño is.
El Niño and its opposite, La Niña, are climate patterns that influence weather around the world. El Niño tends to raise global temperatures, as we saw in 2023, while La Niña events tend to be slightly cooler. The two result in global temperatures fluctuating above and below the warming trend set by climate change.
El Niño starts as warm water builds up along the equator in the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean, off South America.
Typically, tropical Pacific winds blow from the east, exposing cold water along the equator and building up warm water in the western Pacific. Every three to seven years or so, however, these winds relax or turn to blow from the west. When that happens, warm water rushes to the east. The warmer-than-normal water drives more rainfall and alters winds around the world. This is El Niño.
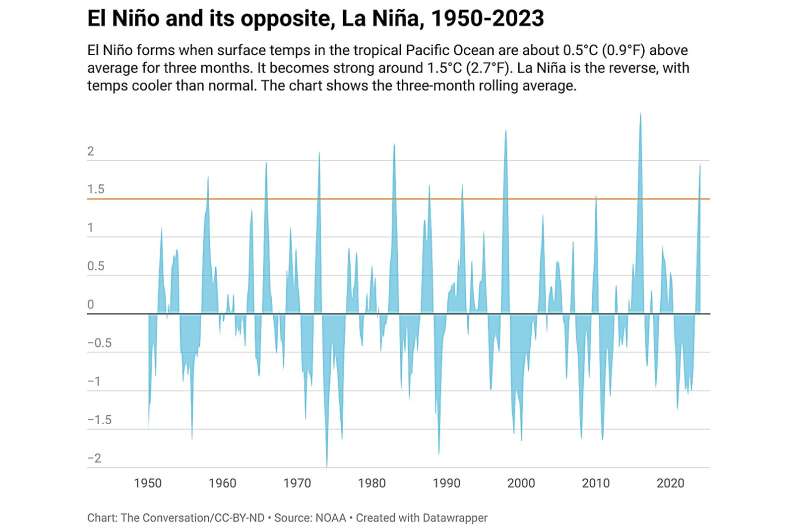
Credit: The Conversation
The water stays warm for several months until, ultimately, it cools or is driven away from the equator by the return of the trade winds.
When the eastern Pacific region along the equator becomes abnormally cold, La Niña has emerged, and global weather patterns change again.
What to expect from El Niño in 2024
While the 2023-24 El Niño event likely peaked in December, it is still strong.
For the rest of winter, forecasts suggest that strong El Niño conditions will likely continue to favor unusual warmth in Canada and the northern United States and occasional stormy conditions across the southern states.
El Niño is likely to end in late spring or early summer, shifting briefly to neutral. There’s a good chance we will see La Niña conditions this fall. But forecasting when that happens and what comes next is harder.
How El Niño develops in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
How an El Niño ends
While it’s easy to tell when an El Niño event reaches its peak, predicting when one will end depends on how the wind blows, and everyday weather affects the winds.
The warm area of surface water that defines El Niño typically becomes more shallow toward spring. In mid-May 1998, at the end of an even stronger El Niño event, there was a time when people fishing in the warm surface water in the eastern tropical Pacific could have touched the cold water layer a few feet below by just jumping in. At that point, it took only a moderate breeze to pull the cold water to the surface, ending the El Niño event.
But exactly when a strong El Niño event reverses varies. A big 1983 El Niño didn’t end until July. And the El Niño in 1987 retreated into the central Pacific but did not fully reverse until December.
As of early February 2024, strong westerly winds were driving warm water from west to east across the equatorial Pacific.
These winds tend to make El Niño last a little longer. However, they’re also likely to drive what little warm water remains along the equator out of the tropics, up and down the coasts of the Americas. The more warm water that is expelled, the greater the chances of full reversal to La Niña conditions in the fall.
Summer and the hurricane risk
Among the more important El Niño effects is its tendency to reduce Atlantic hurricane activity.
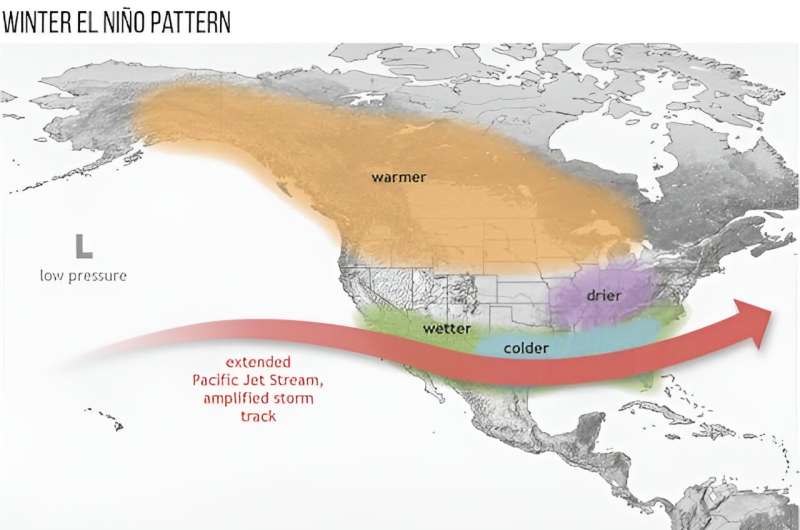
Typical winters under El Niño and La Niña show the striking differences between the two patterns. Not all El Niños turn out this way. Credit: NOAA Climate.gov
El Niño’s Pacific Ocean heat affects upper level winds that blow across the Gulf of Mexico and the tropical Atlantic Ocean. That increases wind shear—the change in wind speed and direction with height—which can tear hurricanes apart.
The 2024 hurricane season likely won’t have El Niño around to help weaken storms. But that doesn’t necessarily mean an active season.
During the 2023 Atlantic hurricane season, El Niño’s effect on the winds was more than offset by abnormally warm Atlantic waters, which fuel hurricanes. The season ended with more storms than average.
The strange El Niño of 2023-24
Although the 2023-24 El Niño event wasn’t the strongest in recent decades, many aspects of it have been unusual.
It followed three years of La Niña conditions, which is unusually long. It also emerged quickly, from March to May 2023. The combination led to weather extremes unseen since perhaps the 1870s.
La Niña cools the tropics but stores warm water in the western Pacific. It also warms the middle latitude oceans by weakening the winds and allowing more sunshine through. After three years of La Niña, the rapid emergence of El Niño helped make the Earth’s surface warmer than in any recent year.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()
Citation:
El Niño is starting to lose strength after fueling a hot, stormy year. An atmospheric scientist explains what’s ahead (2024, February 11)
retrieved 12 February 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-02-el-nio-strength-fueling-hot.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
>>> Read full article>>>
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source : Phys.org – https://phys.org/news/2024-02-el-nio-strength-fueling-hot.html










