
New research on the Milky Way’s central region, “The Brick,” using the JWST, has uncovered a paradox: high levels of CO ice but low star formation rates. These findings challenge established theories about star formation and suggest a reevaluation of molecular processes in our galaxy. (Artist’s concept.) Credit: SciTechDaily.com
UF astronomer Adam Ginsburg harnesses the James Webb Space Telescope to explore a galactic enigma.
In a recent study led by University of Florida astronomer Adam Ginsburg, groundbreaking findings shed light on a mysterious dark region at the center of the Milky Way. The turbulent gas cloud, playfully nicknamed “The Brick” due to its opacity, has sparked lively debates within the scientific community for years.
To decipher its secrets, Ginsburg and his research team, including UF graduate students Desmond Jeff, Savannah Gramze, and Alyssa Bulatek, turned to the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The implications of their observations, published in The Astrophysical Journal, are monumental. The findings not only unearth a paradox within the center of our galaxy but indicate a critical need to re-evaluate established theories regarding star formation.
The Enigma of the Brick
The Brick has been one of the most intriguing and highly studied regions of our galaxies, thanks to its unexpectedly low star formation rate. It has challenged scientists’ expectations for decades: as a cloud full of dense gas, it should be ripe for the birth of new stars. However, it demonstrates an unexpectedly low star formation rate.
Using the JWST’s advanced infrared capabilities, the team of researchers peered into the Brick, discovering a substantial presence of frozen carbon monoxide (CO) there. It harbors a significantly larger amount of CO ice than previously anticipated, carrying profound implications for our understanding of star formation processes.
No one knew how much ice there was in the Galactic Center, according to Ginsburg. “Our observations compellingly demonstrate that ice is very prevalent there, to the point that every observation in the future must take it into account,” he said.
Stars typically emerge when gases are cool, and the significant presence of CO ice should suggest a thriving area for star formation in the Brick. Yet, despite this wealth of CO, Ginsburg and the research team found that the structure defies expectations. The gas inside the Brick is warmer than comparable clouds.

The Galactic Center is full of stars: There are over half a million in this image. Using JWST’s specialized filters and a little bit of Photoshop, the team was able to remove the stars and show only the filamentary nebula of hot gas that permeates the inner Galaxy. (See image below with the stars removed.) Credit: Adam Ginsburg
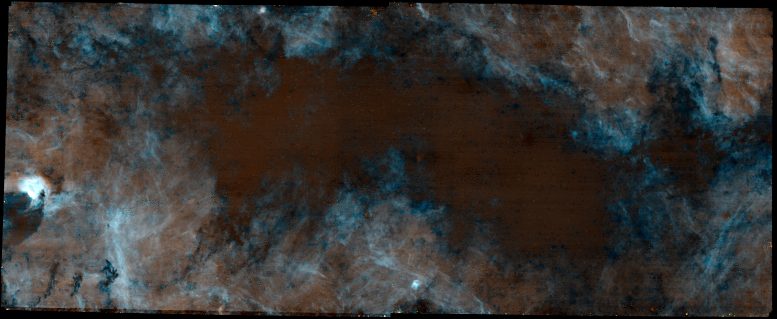
Image of just the filamentary nebula of hot gas that permeates the inner Galaxy. The bright regions are where hydrogen is a hot plasma, glowing from the energy from the massive stars. The Brick is the dark region where that glowing plasma is blocked out. Along the edge of the Brick, the glow is bluer: this blue appearance is caused by the CO ice blocking out the red light, letting only the blue through. Credit: Adam Ginsburg
Challenging Established Theories
These observations challenge our understanding of CO abundance in the center of our galaxy and the critical gas-to-dust ratio there. According to the findings, both measures appear to be lower than previously thought.
“With JWST, we’re opening new paths to measure molecules in the solid phase (ice), while previously we were limited to looking at gas,” said Ginsburg. “This new view gives us a more complete look at where molecules exist and how they are transported.“
Traditionally, the observation of CO has been limited to emission from gas. To unveil the distribution of CO ice within this vast cloud, the researchers required intense backlighting from stars and hot gas. Their findings move beyond the limitations of previous measurements, which were confined to around a hundred stars. The new results encompass over ten thousand stars, providing valuable insights into the nature of interstellar ice.

Adam Ginsburg, PhD. Credit: Adam Ginsburg
Since the molecules present in our Solar System today were, at some point, likely ice on small dust grains that combined to form planets and comets, the discovery also marks a leap forward toward understanding the origins of the molecules that shape our cosmic surroundings.
These are just the team’s initial findings from a small fraction of their JWST observations of the Brick. Looking ahead, Ginsburg sets his sights on a more extensive survey of celestial ices.
“We don’t know, for example, the relative amounts of CO, water, CO2, and complex molecules,” said Ginsburg. “With spectroscopy, we can measure those and get some sense of how chemistry progresses over time in these clouds.”
Advancements in Cosmic Exploration
With the advent of the JWST and its advanced filters, Ginsburg and his colleagues are presented with their most promising opportunity yet to expand our cosmic exploration.
In a recent study led by University of Florida astronomer Adam Ginsburg, groundbreaking findings shed light on a mysterious dark region at the center of the Milky Way. The turbulent gas cloud, playfully nicknamed “The Brick” due to its opacity, has sparked lively debates within the scientific community for years.
To decipher its secrets, Ginsburg and his research team, including UF graduate students Desmond Jeff, Savannah Gramze, and Alyssa Bulatek, turned to the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The implications of their observations, published in The Astrophysical Journal, are monumental. The findings not only unearth a paradox within the center of our galaxy but indicate a critical need to re-evaluate established theories regarding star formation.
The Brick has been one of the most intriguing and highly studied regions of our galaxies, thanks to its unexpectedly low star formation rate. It has challenged scientists’ expectations for decades: as a cloud full of dense gas, it should be ripe for the birth of new stars. However, it demonstrates an unexpectedly low star formation rate.
Using the JWST’s advanced infrared capabilities, the team of researchers peered into the Brick, discovering a substantial presence of frozen carbon monoxide (CO) there. It harbors a significantly larger amount of CO ice than previously anticipated, carrying profound implications for our understanding of star formation processes.
No one knew how much ice there was in the Galactic Center, according to Ginsburg. “Our observations compellingly demonstrate that ice is very prevalent there, to the point that every observation in the future must take it into account,” he said.
Stars typically emerge when gases are cool, and the significant presence of CO ice should suggest a thriving area for star formation in the Brick. Yet, despite this wealth of CO, Ginsburg and the research team found that the structure defies expectations. The gas inside the Brick is warmer than comparable clouds.
These observations challenge our understanding of CO abundance in the center of our galaxy and the critical gas-to-dust ratio there. According to the findings, both measures appear to be lower than previously thought.
“With JWST, we’re opening new paths to measure molecules in the solid phase (ice), while previously we were limited to looking at gas,” said Ginsburg. “This new view gives us a more complete look at where molecules exist and how they are transported.“
Traditionally, the observation of CO has been limited to emission from gas. To unveil the distribution of CO ice within this vast cloud, the researchers required intense backlighting from stars and hot gas. Their findings move beyond the limitations of previous measurements, which were confined to around a hundred stars. The new results encompass over ten thousand stars, providing valuable insights into the nature of interstellar ice.
Since the molecules present in our Solar System today were, at some point, likely ice on small dust grains that combined to form planets and comets, the discovery also marks a leap forward toward understanding the origins of the molecules that shape our cosmic surroundings.
These are just the team’s initial findings from a small fraction of their JWST observations of the Brick. Looking ahead, Ginsburg sets his sights on a more extensive survey of celestial ices.
“We don’t know, for example, the relative amounts of CO, water, CO2, and complex molecules,” said Ginsburg. “With spectroscopy, we can measure those and get some sense of how chemistry progresses over time in these clouds.”
With the advent of the JWST and its advanced filters, Ginsburg and his colleagues are presented with their most promising opportunity yet to expand our cosmic exploration.
Reference: “JWST Reveals Widespread CO Ice and Gas Absorption in the Galactic Center Cloud G0.253+0.016” by Adam Ginsburg, Ashley T. Barnes, Cara D. Battersby, Alyssa Bulatek, Savannah Gramze, Jonathan D. Henshaw, Desmond Jeff, Xing Lu, E. A. C. Mills and Daniel L. Walker, 4 December 2023, The Astrophysical Journal.
DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/acfc34
>>> Read full article>>>
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source : SciTechDaily – https://scitechdaily.com/galactic-paradox-webb-telescope-unravels-mysterious-secrets-of-the-brick/










