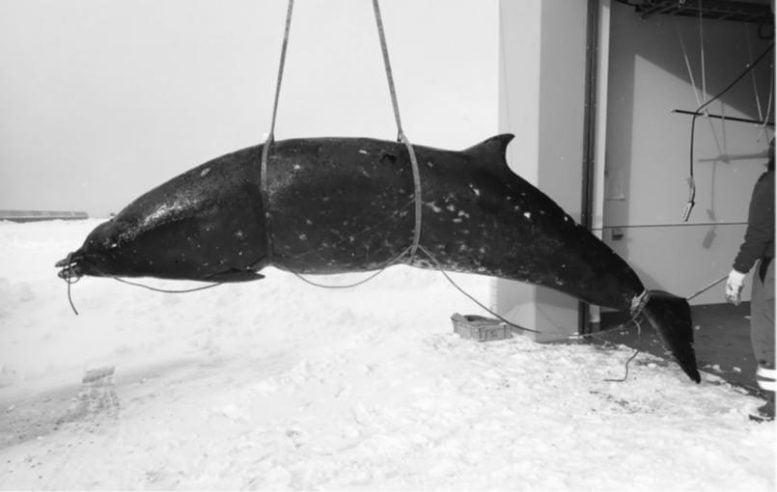

Left side full-body photo of the ginkgo-toothed beaked whale described in this study. Credit: Wojtek Bachara, Kuroda Mika, et al. Aquatic Mammals. July 9, 2023
The little-known ginkgo-toothed beaked whale has a wider range than previously understood, extending to the chilly waters of the North Pacific.
Cetaceans, widely known as fully aquatic animals, encompass whales, dolphins, and porpoises. This group includes over 90 existing species, categorized into baleen whales (Mysticeti) and toothed whales (Odontoceti). Specifically, toothed whales, distinguished by their teeth, encompass various species, including the lesser-known genus Mesoplodon. These animals typically inhabit offshore oceanic areas and seldom surface, making their distribution and ecology relatively unknown.
A team of researchers, including Hokkaido University’s Assistant Professor Kuroda Mika at the Field Science Center for Northern Biosphere and Professor Matsuishi Takashi Fritz at the Faculty of Fisheries Sciences, recently reported the discovery of a stranded ginkgo-toothed beaked whale from the coast of Yakumo, Southern Hokkaido. Their findings were published in the journal Aquatic Mammals.
Characteristics of the Mesoplodon Genus
“The genus Mesoplodon consists of over 15 known species, and is the largest genus of Ziphiidae,” Kuroda explains. “The different species in this genus can be identified by the shape of the head and by specific teeth in the males. Males of the ginkgo-toothed beaked whale, Mesoplodon ginkgodens, possess 10-cm-wide teeth shaped like the leaves of the ginkgo tree, Ginkgo biloba.”
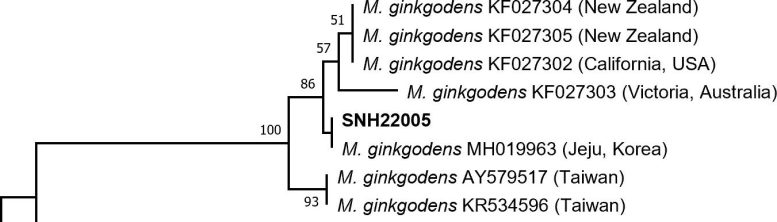
Portion of the phylogenetic tree showing that the whale in this study (SNH22005) is placed in the Mesoplodon ginkgodens clade. Credit: Wojtek Bachara, Kuroda Mika, et al. Aquatic Mammals. July 9, 2023
Everything we know about ginkgo-toothed beaked whales comes almost exclusively from 95 individuals from 88 separate whale stranding events. Of these, 30 stranding events occurred across Japan.
On February 4, 2022, a whale beaching in Yakumo town, Hokkaido, was reported. The dead whale body was transported to Hakodate Research Centre for Fisheries and Oceans for measurement and a necropsy. The whale was a male measuring 477 cm in body length, and was in early stages of decomposition, indicating it had been dead for some time. Its morphology was consistent with those for M. ginkgodens; furthermore, genetic analysis of mitochondrial DNA placed this specimen within the clade for M. ginkgodens, with one identical sequence.
Geographical Range of Strandings
Previous strandings have occurred in a wide range of locations, including Japan, the US West Coast, Australia, the Galapagos Islands, Thailand, New Zealand, Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, China, South Korea, and Mexico—all in temperate, subtropical, and tropical waters. This study is the first report of Mesoplodon ginkgodens from the colder waters of the North Pacific.
“Another stranding that might have been a ginkgo-toothed beaked whale was reported on November 29, 2021, but the specimen was lost due to bad weather,” said Kuroda. “Our findings indicate that these whales may have migrated near Hokkaido during the winter.”
Reference: “Northernmost Record of the Ginkgo-Toothed Beaked Whale (Mesoplodon ginkgodens)” by Wojtek Bachara, Kuroda Mika, et al., 9 July 2023, Aquatic Mammals.
DOI: 10.1578/AM.49.4.2023.356
>>> Read full article>>>
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source : SciTechDaily – https://scitechdaily.com/marine-mystery-scientists-discover-little-known-beaked-whale-in-cold-waters-of-japan/










