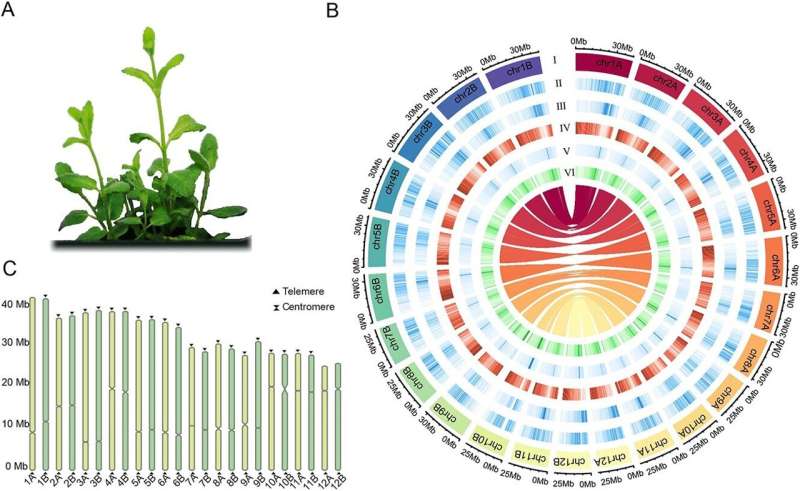
Overview of the genomic features of M. suaveolens. a) Image of M. suaveolens. b) Circos plot of M. suaveolens haplotype-resolved gap-free genomic features. I: Chromosome length. II: LTR/Copia coverage. III: LTR/Gypsy elements. IV: Gene density. V: Repeat sequence density. VI: GC content. The innermost part of the plot represents the collinear relationship between the M. suaveolens haplotype-resolved genomes. c) Location of the predicted centromere region and identified telomere sequences in M. suaveolens. Credit: Horticulture Research (2024). DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae022
Mentha suaveolens, commonly known as pineapple mint, is valued for its distinct aroma and medicinal properties, which are attributed to its essential oils.
Despite its importance, understanding the genetic basis of these traits has been challenging due to the complexity of the Mentha genome, characterized by high heterozygosity and numerous structural variations. A comprehensive study of the Mentha genome was essential to uncover the genetic factors influencing its unique characteristics.
Researchers from the Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, in collaboration with several other institutions, successfully assembled a haplotype-resolved, gap-free genome of Mentha suaveolens, also known as pineapple mint.
Utilizing advanced sequencing technologies, the team shed light on the genetic diversity and structural variations within the genome, providing a valuable resource for future genetic and breeding research. The study is published in the journal Horticulture Research.
The study presents the first high-quality, haplotype-resolved genome assembly for Mentha suaveolens, with a genome size of 414.3 Mb and 31,251 coding genes. By integrating data from various sequencing platforms, the researchers resolved two complete haplotypic assemblies, each nearly fully annotated for telomeres and centromeres.
Notably, the analysis revealed 41,135 structural variations, including deletions, insertions, duplications, and translocations, many of which impact genes involved in terpenoid biosynthesis.
One significant finding is the predominance of piperitenone oxide among the volatile compounds produced by M. suaveolens, as opposed to menthol, which is more common in other Mentha species.
The study identified three genes encoding isopiperitenone reductase (ISPR), a key enzyme in menthol biosynthesis, but found that their low transcription levels likely lead to the accumulation of piperitenone oxide instead.
Dr. Chi Song, one of the leading researchers, stated, “The completion of the gap-free genome for Mentha suaveolens represents a significant milestone in plant genomics. This comprehensive genetic map provides a foundation for exploring the molecular mechanisms underlying the unique properties of pineapple mint, which could lead to innovative applications in medicine and agriculture.”
The gap-free genome assembly of Mentha suaveolens paves the way for genetic research and breeding to enhance its medicinal and aromatic qualities. Understanding the genetic basis of terpenoid biosynthesis enables targeted strategies to optimize valuable compounds like piperitenone oxide.
This research advances plant genomics and has significant potential to improve the cultivation and commercial value of Mentha species.
More information:
Hanting Yang et al, A haplotype-resolved gap-free genome assembly provides novel insight into monoterpenoid diversification in Mentha suaveolens ‘Variegata’, Horticulture Research (2024). DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae022
Provided by
TranSpread
Citation:
Pineapple mint’s genetic blueprint: A comprehensive genome assembly (2024, May 23)
retrieved 23 May 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-05-pineapple-mint-genetic-blueprint-comprehensive.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
>>> Read full article>>>
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source : Phys.org – https://phys.org/news/2024-05-pineapple-mint-genetic-blueprint-comprehensive.html