Diagram showing how wax structure reflect light. Credit: Rox Middleton
Tiny external structures in the wax coating of blueberries give them their blue color, researchers at the University of Bristol can reveal. This applies to a lot of fruits that are the same color including damsons, sloes and juniper berries.
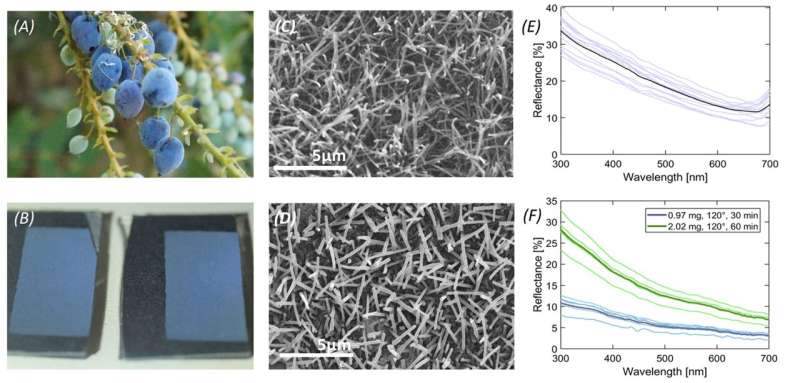
In the study, published in Science Advances, researchers show why blueberries are blue despite the dark red color of the pigments in the fruit skin. Their blue color is instead provided by a layer of wax that surrounds the fruit which is made up of miniature structures that scatter blue and UV light. This gives blueberries their blue appearance to humans and blue-UV to birds. The chromatic blue-UV reflectance arises from the interaction of the randomly arranged crystal structures of the epicuticular wax with light.
Rox Middleton, Research Fellow at Bristol’s School of Biological Sciences, explained, “The blue of blueberries can’t be ‘extracted’ by squishing—because it isn’t located in the pigmented juice that can be squeezed from the fruit. That was why we knew that there must be something strange about the color.
“So we removed the wax and re-crystallized it on card and in doing so we were able to create a brand new blue-UV coating.”

Blueberries. Credit: Rox Middleton
The ultra-thin colorant is around two microns thick, and although less reflective, it’s visibly blue and reflects UV well, possibly paving the way for new colorant methods.
“It shows that nature has evolved to use a really neat trick, an ultrathin layer for an important colorant,” added Rox.
Most plants are coated in a thin layer of wax which has multiple functions, many of which scientists still don’t understand. They know that it can be very effective as a hydrophobic, self-cleaning coating, but it’s only now they realize how important the structure is for visible coloration.
Now the team plans to look at easier ways of recreating the coating and applying it. This could lead to a more sustainable, biocompatible and even edible UV and blue-reflective paint.
Furthermore, these coatings could have the same multiple functions as natural biological ones that protect plants.
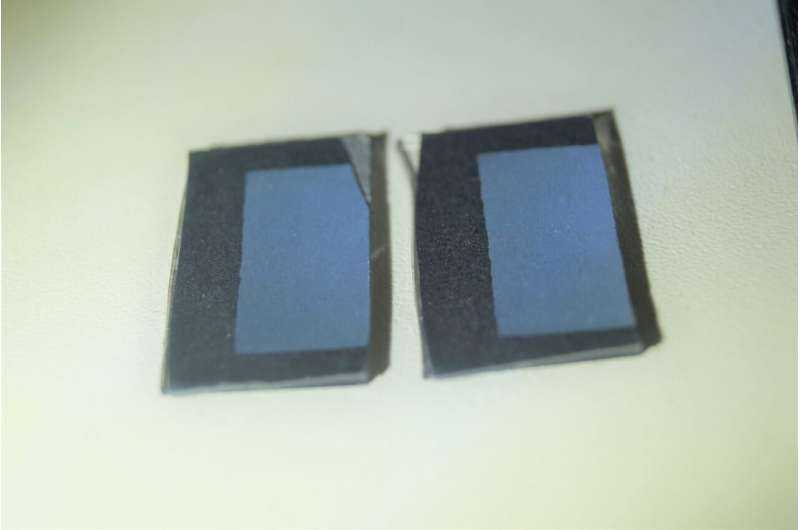

Deposited wax. Credit: Rox Middleton
Rox added, “It was really interesting to find that there was an unknown coloration mechanism right under our noses, on popular fruits that we grow and eat all the time.
“It was even more exciting to be able to reproduce that color by harvesting the wax to make a new blue coating that no one’s seen before.
“Building all that functionality of this natural wax into artificially engineered materials is the dream.”
More information:
Rox Middleton et al, Self-assembled, Disordered Structural Color from Fruit Wax Bloom, Science Advances (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adk4219. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adk4219
Citation:
Scientists reveal why blueberries are blue (2024, February 7)
retrieved 7 February 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-02-scientists-reveal-blueberries-blue.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
>>> Read full article>>>
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source : Phys.org – https://phys.org/news/2024-02-scientists-reveal-blueberries-blue.html










