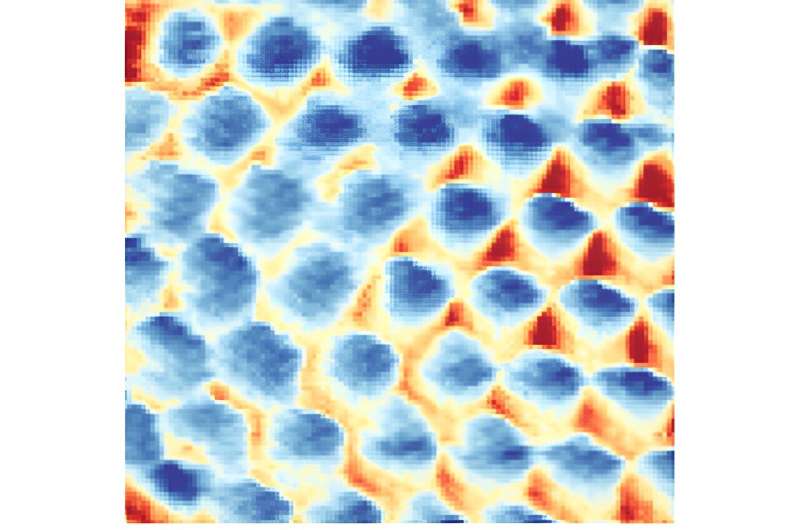
An image of a triangular Wigner crystal taken by scanning tunneling microscope. Researchers have unveiled an elusive crystal that is formed purely from the repulsive nature of electrons. Each site (blue circular region) contains a single localized electron. Image by Yen-Chen Tsui and team, Princeton University. Credit: Yen-Chen Tsui, Princeton University
Electrons—the infinitesimally small particles that are known to zip around atoms—continue to amaze scientists despite the more than a century that scientists have studied them. Now, physicists at Princeton University have pushed the boundaries of our understanding of these minute particles by visualizing, for the first time, direct evidence for what is known as the Wigner crystal—a strange kind of matter that is made entirely of electrons.
The finding, published in Nature, confirms a 90-year-old theory that electrons can assemble into a crystal-like formation of their own, without the need to coalesce around atoms. The research could help lead to the discovery of new quantum phases of matter when electrons behave collectively.
“The Wigner crystal is one of the most fascinating quantum phases of matter that has been predicted and the subject of numerous studies claiming to have found, at best, indirect evidence for its formation,” said Al Yazdani, the James S. McDonnell Distinguished University Professor in Physics at Princeton University and the senior author of the study. “Visualizing this crystal allows us not only to watch its formation, confirming many of its properties, but we can also study it in ways you couldn’t in the past.”
In the 1930s, Eugene Wigner, a Princeton professor of physics and winner of the 1963 Nobel Prize for his work in quantum symmetry principles, wrote a paper in which he proposed the then-revolutionary idea that interaction among electrons could lead to their spontaneous arrangement into a crystal-like configuration, or lattice, of closely packed electrons. This could only occur, he theorized, because of their mutual repulsion and under conditions of low densities and extremely cold temperatures.
“When you think of a crystal, you typically think of an attraction between atoms as a stabilizing force, but this crystal forms purely because of the repulsion between electrons,” said Yazdani, who is the inaugural co-director of the Princeton Quantum Institute and director of the Princeton Center for Complex Materials.
For a long time, however, Wigner’s strange electron crystal remained in the realm of theory. It was not until a series of much later experiments that the concept of an electron crystal transformed from conjecture to reality. The first of these was conducted in the 1970s when scientists at Bell Laboratories in New Jersey created a “classical” electron crystal by spraying electrons on the surface of helium and found that they responded in a rigid manner like a crystal.
However, the electrons in these experiments were very far apart and behaved more like individual particles than a cohesive structure. A true Wigner crystal, instead of following the familiar laws of physics in the everyday world, would follow the laws of quantum physics, in which the electrons would act not like individual particles but more like a single wave.
This led to a whole series of experiments over the next decades that proposed various ways to create quantum Wigner crystals. These experiments were greatly advanced in the 1980s and 1990s when physicists discovered how to confine electrons’ motion to atomically thin layers using semiconductors.
The application of a magnetic field to such layered structures also makes electrons move in a circle, creating favorable conditions for crystallization. However, these experiments were never able to observe the crystal directly. They were only able to suggest its existence or indirectly infer it from how electrons flow through the semiconductor.
The video describes the melting processes of an electron Wigner crystal into electron-liquid phases. Credit: Princeton University
“There are literally hundreds of scientific papers that study these effects and claim that the results must be due to the Wigner crystal,” Yazdani said, “but one can’t be sure because none of these experiments actually see the crystal.”
An equally important consideration, Yazdani noted, is that what some researchers think is evidence of a Wigner crystal could be the result of imperfections or other periodic structures inherent to the materials used in the experiments.
“If there are any imperfections or some form of periodic substructure in the material, it is possible to trap electrons and find experimental signatures that are not due to the formation of a self-organized ordered Wigner crystal itself, but due to electrons ‘stuck’ near an imperfection or trapped because of the material’s structure,” he said.
With these considerations in mind, Yazdani and his research team set about to see whether they could directly image the Wigner crystal using a scanning tunneling microscope (STM), a device that relies on a technique called “quantum tunneling” rather than light to view the atomic and subatomic world.
They also decided to use graphene, an amazing material that was discovered in the 21st century and has been used in many experiments involving novel quantum phenomena. To successfully conduct the experiment, however, the researchers had to make the graphene as pristine and as devoid of imperfections as possible. This was key to eliminating the possibility of any electron crystals forming because of material imperfections.
The results were impressive. “Our group has been able to make unprecedentedly clean samples that made this work possible,” Yazdani said. “With our microscope we can confirm that the samples are without any atomic imperfection in the graphene atomic lattice or foreign atoms on its surface over regions with hundreds of thousands of atoms.”
To make pure graphene, the researchers exfoliated two carbon sheets of graphene in a configuration that is called Bernal-stacked bilayer graphene (BLG). They then cooled the sample down to extremely low temperatures—just a fraction of a degree above absolute zero—and applied a magnetic field perpendicular to the sample, which created a two-dimensional electron gas system within the thin layers of graphene. With this, they could tune the density of the electrons between the two layers.
“In our experiment, we can image the system as we tune the number of electrons per unit area,” said Yen-Chen Tsui, a graduate student in physics and the first author of the paper. “Just by changing the density, you can initiate this phase transition and find electrons spontaneously form into an ordered crystal.”
This happens, Tsui explained, because at low densities, the electrons are far apart from each other—and they’re situated in a disordered, disorganized fashion. However, as you increase the density, which brings the electrons closer together, their natural repulsive tendencies kick in, and they start to form an organized lattice. Then, as you increase the density further, the crystalline phase will melt into an electron liquid.
Minhao He, a postdoctoral researcher and co-first author of the paper, explained this process in greater detail. “There is an inherent repulsion between the electrons,” he said. “They want to push each other away, but in the meantime, the electrons cannot be infinitely apart due to the finite density. The result is that they form a closely packed, regularized lattice structure, with each of the localized electron occupying a certain amount of space.”
When this transition formed, the researchers were able to visualize it using the STM. “Our work provides the first direct images of this crystal. We proved the crystal is really there, and we can see it,” said Tsui.
However, just visualizing the crystal wasn’t the end of the experiment. A concrete image of the crystal allowed them to distinguish some of the crystal’s characteristics. They discovered that the crystal is triangular in configuration and that it can be continuously tuned with the density of the particles. This led to the realization that the Wigner crystal is actually quite stable over a very long range, a conclusion that is contrary to what many scientists have surmised.
“By being able to tune its lattice constant continuously, the experiment proved that the crystal structure is the result of the pure repulsion between the electrons,” said Yazdani.
The researchers also discovered several other interesting phenomena that will no doubt warrant further investigation in the future. They found that the location to which each electron is localized in the lattice appears in the images with a certain amount of “blurring,” as if the location is not defined by a point but a range position in which the electrons are confined in the lattice. The paper described this as the “zero-point” motion of electrons, a phenomenon related to the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. The extent of this blurriness reflects the quantum nature of the Wigner crystal.
“Electrons, even when frozen into a Wigner crystal, should exhibit strong zero-point motion,” said Yazdani. “It turns out this quantum motion covers a third of the distance between them, making the Wigner crystal a novel quantum crystal.”
Yazdani and his team are also examining how the Wigner crystal melts and transitions into other exotic liquid phases of interacting electrons in a magnetic field. The researchers hope to image these phases just as they have imaged the Wigner crystal.
More information:
Ali Yazdani, Direct observation of a magnetic-field-induced Wigner crystal, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07212-7. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07212-7
Journal information:
Nature
Citation:
Quantum crystal of frozen electrons—the Wigner crystal—is visualized for the first time (2024, April 10)
retrieved 10 April 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-04-quantum-crystal-frozen-electrons-wigner.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
>>> Read full article>>>
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source : Phys.org – https://phys.org/news/2024-04-quantum-crystal-frozen-electrons-wigner.html










